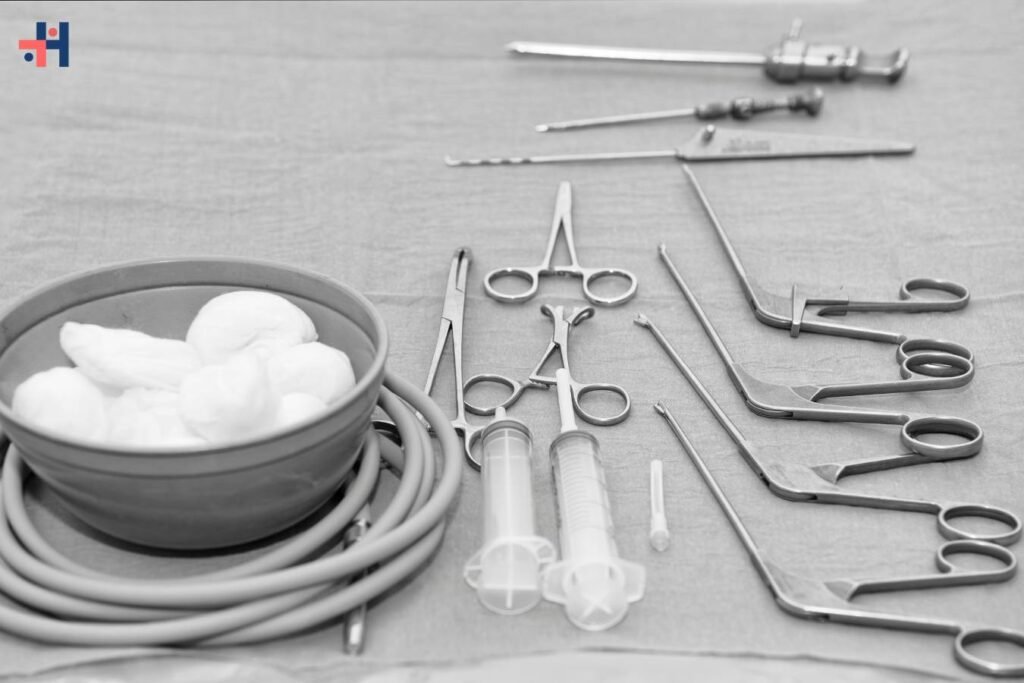
Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, has revolutionized the field of orthopedics by allowing surgeons to diagnose and treat joint problems with precision and minimal trauma to surrounding tissues. At the heart of successful arthroscopic surgery are specialized instruments designed to facilitate visualization, manipulation, and repair within the joint space. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of arthroscopy instruments, exploring their types, functions, and advancements in technology.
Understanding Arthroscopy:
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat joint conditions, such as torn ligaments, cartilage damage, and joint inflammation. During arthroscopy, a small camera, called an arthroscope, is inserted into the joint through a small incision. The arthroscope transmits images of the joint to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to visualize and assess the condition of the joint in real-time.
Types of Arthroscopy Instruments:
1. Arthroscope:
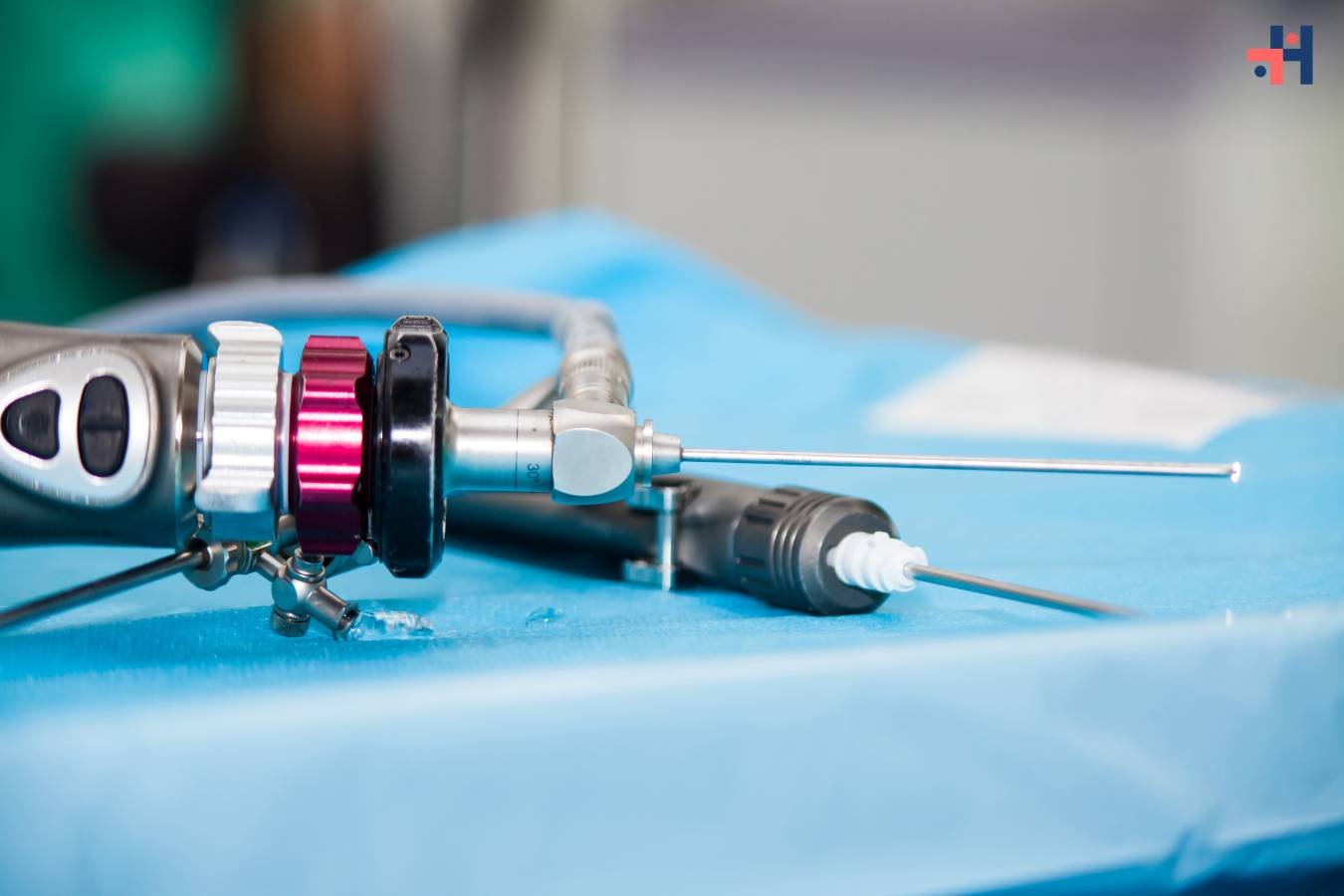
The arthroscope is a thin, tube-like instrument equipped with a camera and light source. It allows the surgeon to visualize the interior of the joint and guide other instruments during surgery.
2. Probes and Hooks:
Probes and hooks are used to manipulate and explore structures within the joint, such as cartilage and ligaments. They come in various sizes and shapes to accommodate different anatomical structures.
3. Graspers and Forceps:
Graspers and forceps are used to grasp, hold, and manipulate tissue within the joint. They may have serrated jaws or atraumatic tips to ensure a secure grip without causing damage to surrounding structures.
4. Shavers and Burrs:
Shavers and burrs are powered instruments used to remove damaged tissue, such as torn cartilage or inflamed synovium, from the joint. They utilize rotating blades or abrasive surfaces to precisely resect tissue while minimizing trauma to healthy structures.
5. Suture Passers and Anchors:
Suture passers and anchors are used to repair and secure torn ligaments or tendons within the joint. They allow the surgeon to pass sutures through tissue and anchor them to the bone, restoring stability and function to the joint.
6. Fluid Management Systems:
Fluid management systems are essential for maintaining clear visualization within the joint during arthroscopy. They control the flow of irrigation fluid and suction debris and fluid from the joint, ensuring optimal surgical conditions.
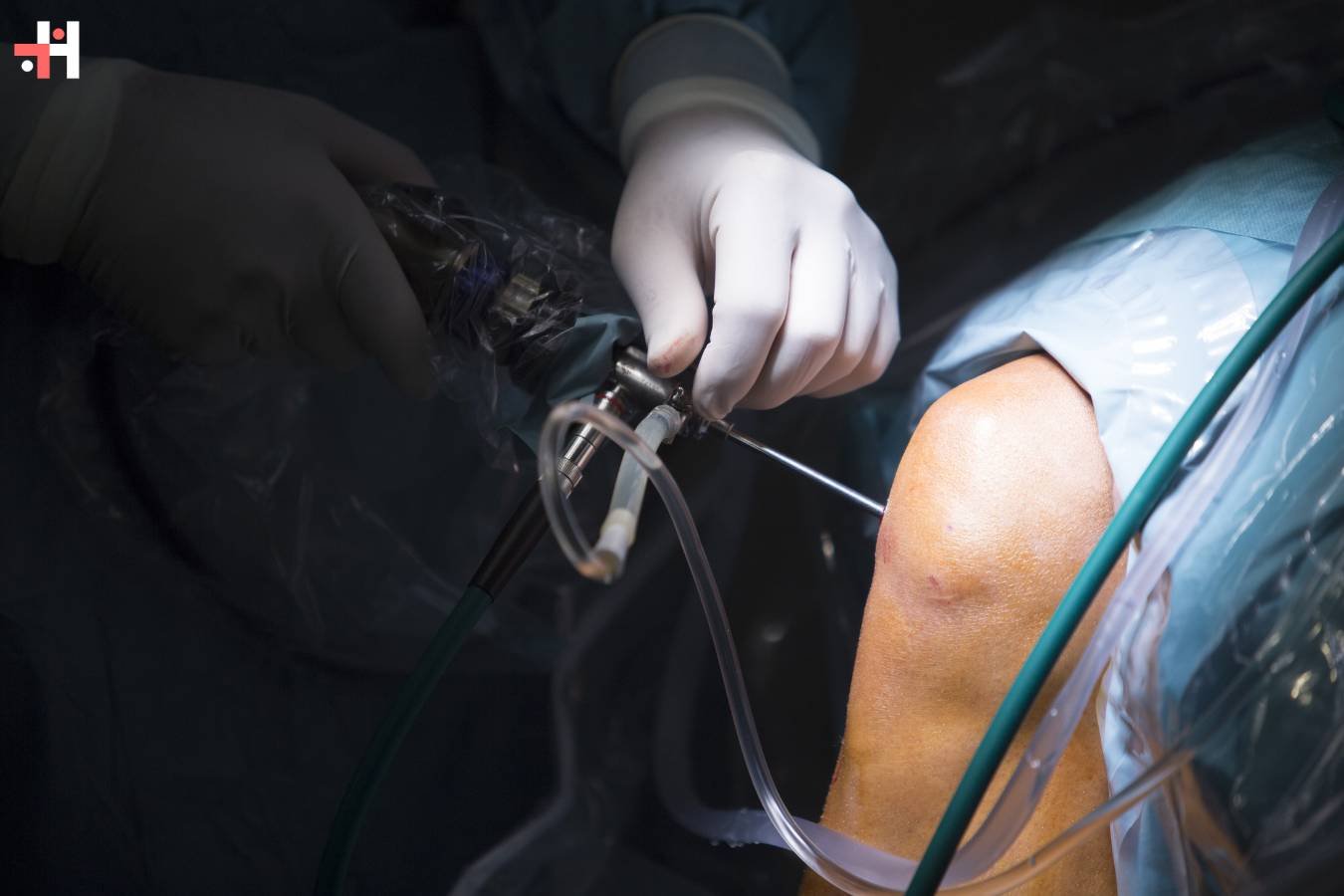
Advancements in Arthroscopy Instrumentation:
1. High-Definition Imaging:
Recent advancements in arthroscopic cameras and monitors have led to the widespread adoption of high-definition imaging systems. These systems provide surgeons with enhanced clarity and detail, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
2. Minimally Invasive Approaches:
Innovations in instrument design and surgical techniques have facilitated the development of minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures. Smaller incisions, specialized instruments, and advanced visualization technology have contributed to reduced post-operative pain, faster recovery times, and improved patient outcomes.
3. Navigation Systems:
Navigation systems utilize real-time imaging and computer-assisted technology to provide surgeons with precise guidance during arthroscopic procedures. These systems allow for accurate measurement, planning, and execution of surgical maneuvers, resulting in improved surgical accuracy and outcomes.
4. Biologics and Regenerative Therapies:
The integration of biologics, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), into arthroscopic procedures holds promise for enhancing tissue repair and regeneration. These therapies aim to harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms to promote tissue healing and regeneration within the joint.
5. Disposable Instruments:
The use of disposable arthroscopy instruments has gained popularity due to their convenience, sterility, and cost-effectiveness. Disposable instruments eliminate the need for reprocessing and sterilization, reducing the risk of cross-contamination and surgical site infections.
Also Read: The World of Microsurgical Instruments: Precision Tools for Medical Advancements
Considerations for Selecting Arthroscopy Instruments:
1. Surgical Indication:
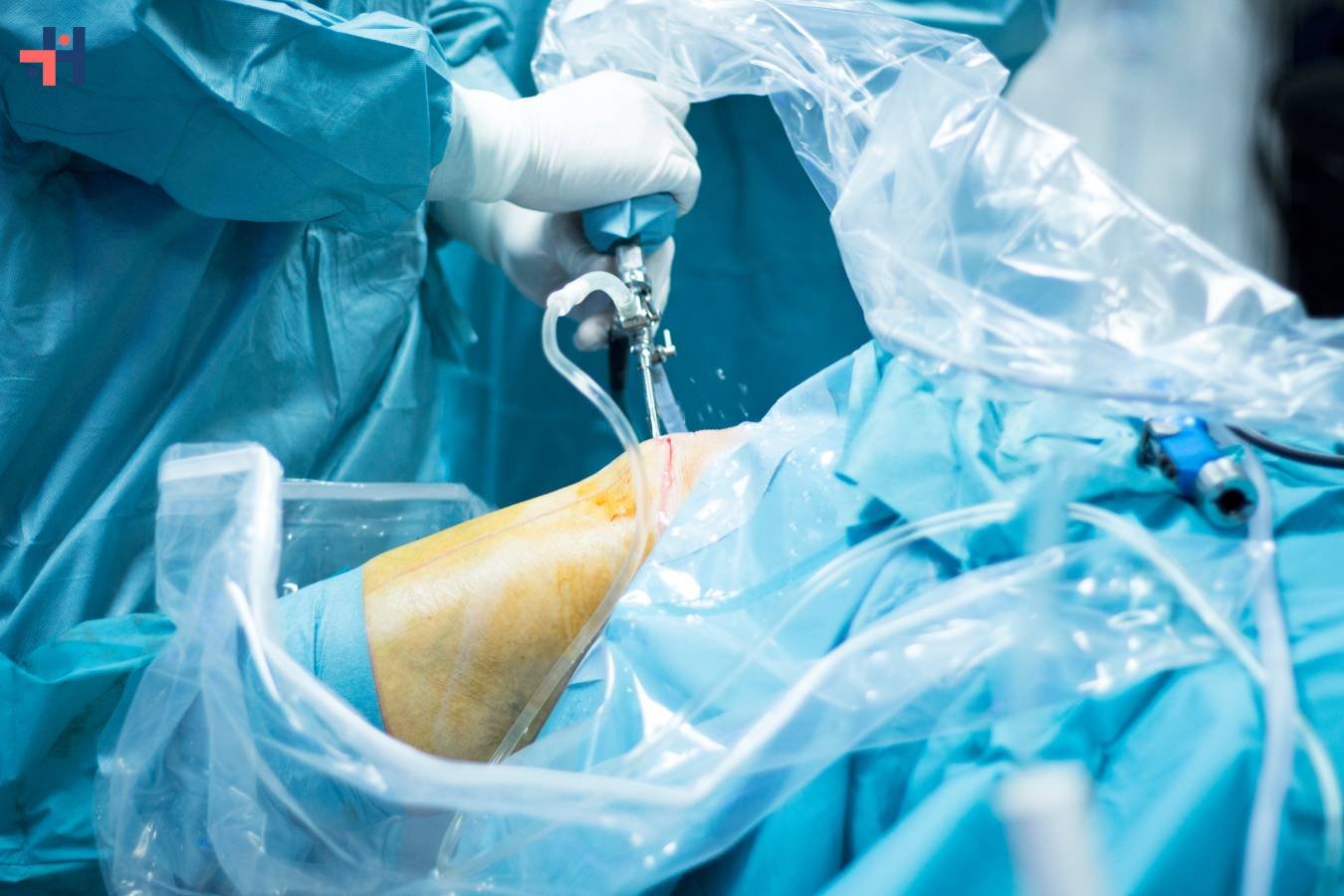
The choice of arthroscopy instruments depends on the specific surgical indication and the anatomical structures involved. Surgeons should select instruments that are appropriate for the procedure and tailored to the patient’s individual needs.
2. Surgeon Preference:
Surgeons may have preferences for certain brands or types of arthroscopy instruments based on their experience, training, and familiarity with specific instrument designs and functionalities.
3. Quality and Reliability:
Quality and reliability are paramount when selecting arthroscopy instruments. Surgeons should choose instruments from reputable manufacturers known for their precision engineering, durability, and adherence to safety standards.
4. Compatibility and Integration:
Arthroscopy instruments should be compatible with existing arthroscopic systems and equipment, ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance during surgery.
5. Training and Support:
Adequate training and technical support are essential for maximizing the effectiveness and safety of arthroscopy instruments. Surgeons should receive comprehensive training on instrument use, maintenance, and troubleshooting to ensure optimal surgical outcomes.
Conclusion:
Arthroscopy instruments play a crucial role in the success of arthroscopic surgery, enabling surgeons to diagnose and treat joint conditions with precision and minimal invasiveness. With ongoing advancements in technology and instrumentation, the future of arthroscopy holds promise for further improvements in patient outcomes and the treatment of joint disorders. By understanding the types, functions, and considerations for selecting arthroscopy instruments, medical professionals can enhance their surgical skills and provide optimal care for patients undergoing arthroscopic procedures.