Biomedical engineering is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that merges principles of engineering with medical and biological sciences to improve healthcare. By designing and developing advanced medical devices, diagnostics, and therapeutic technologies, biomedical engineers play a crucial role in transforming patient care and medical treatments. This article delves into the fundamentals of biomedical engineering, its key applications, and the future trends shaping this exciting field.
What is Biomedical Engineering?
Biomedical Engineering (BME) is a multidisciplinary field that applies engineering principles and techniques to solve problems in medicine and biology. It involves the development of technologies and systems that enhance the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases. Biomedical engineers work at the intersection of engineering, biology, and medicine to create innovative solutions that improve patient outcomes and advance healthcare practices.
Core Areas
BME encompasses several core areas, each focusing on different aspects of medical technology and healthcare:
Medical Devices and Instrumentation
Medical devices and instrumentation are central to biomedical engineering. Engineers in this area design and develop tools and equipment used in diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment. Examples include:
- Imaging Devices: MRI machines, CT scanners, and ultrasound equipment that provide detailed images of internal structures.
- Diagnostic Tools: Blood glucose meters, pregnancy tests, and genetic testing kits.
- Therapeutic Devices: Pacemakers, prosthetics, and infusion pumps that aid in treatment and rehabilitation.
Biomaterials
Biomaterials are materials engineered for use in medical applications that interact with biological systems. This area focuses on designing materials that are biocompatible and can support or replace damaged tissues. Examples include:
- Implants: Artificial joints, dental implants, and vascular stents.
- Tissue Engineering: Creating scaffolds for tissue regeneration and developing bioengineered organs.
Biomechanics
Biomechanics applies principles of mechanics to understand the forces and movements within the human body. Engineers in this field study how mechanical forces affect biological tissues and develop solutions for improving physical function. Key applications include:
- Orthopedic Devices: Braces, prosthetics, and orthotic supports.
- Rehabilitation Engineering: Technologies for physical therapy and rehabilitation, such as robotic exoskeletons.
Biomedical Imaging
Biomedical imaging involves the development and application of techniques to visualize the internal structures and processes of the body. This area focuses on enhancing imaging technologies for better diagnosis and treatment planning. Techniques include:
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
Bioinformatics and computational biology use algorithms, data analysis, and modeling to understand biological systems and processes. This area involves:
- Genomic Data Analysis: Studying genetic information to identify disease markers and develop personalized treatments.
- Medical Data Analysis: Using big data to improve healthcare outcomes and predictive models.
Applications of Biomedical Engineering
BME has a profound impact on various aspects of healthcare and medicine:
Healthcare Technology
Biomedical engineers develop cutting-edge technologies that enhance patient care, including advanced imaging systems, robotic surgery tools, and wearable health monitors. These innovations improve diagnostic accuracy, treatment effectiveness, and patient comfort.
Medical Devices
Medical devices designed by biomedical engineers play a critical role in modern medicine. Devices such as artificial organs, insulin pumps, and cardiac defibrillators are essential for managing chronic conditions and improving patients’ quality of life.
Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
Biomedical engineering contributes to the development of diagnostic tools and therapies for a wide range of diseases. Advances in genomics and personalized medicine allow for more precise and effective treatments tailored to individual patients.
Rehabilitation and Prosthetics
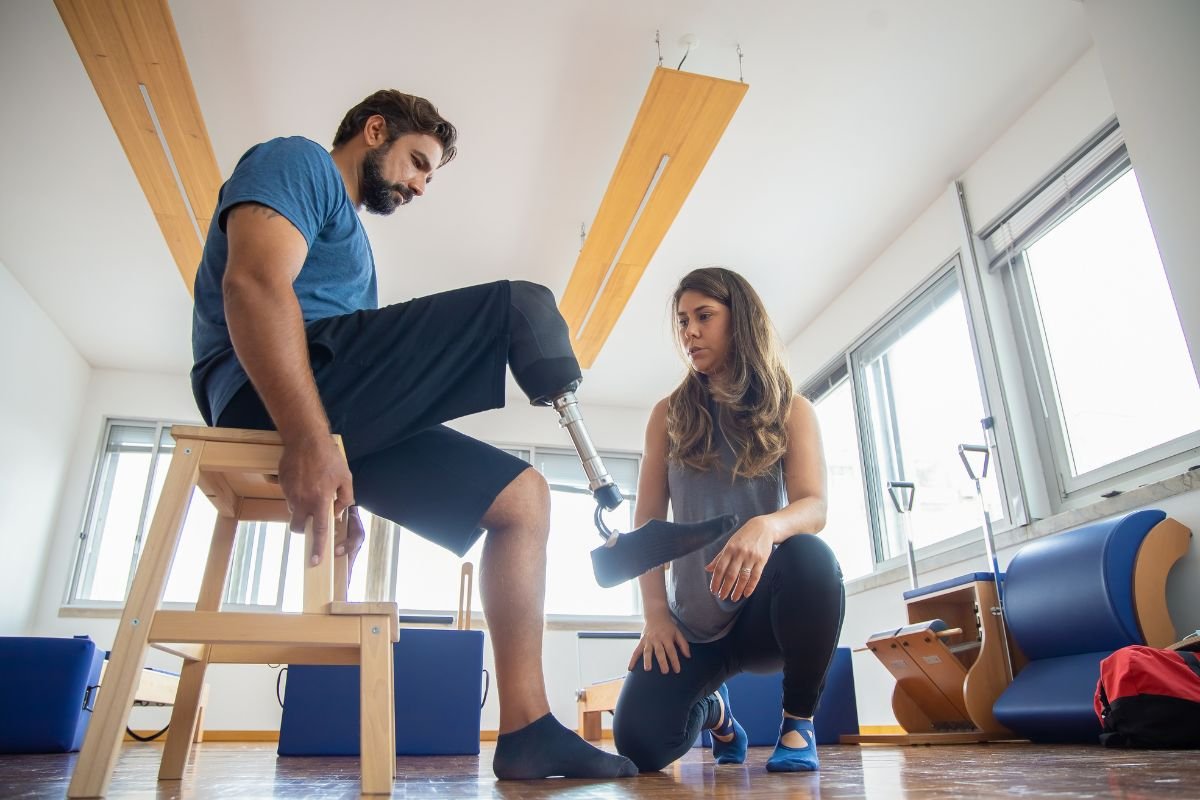

Biomedical engineers design rehabilitation technologies and prosthetic devices that aid in recovery and enhance mobility for individuals with disabilities. Innovations in this area include advanced prosthetic limbs, exoskeletons, and rehabilitation robots.
Challenges and Considerations
While BME offers tremendous potential, several challenges must be addressed:
Regulatory and Safety Issues
Ensuring that medical devices and technologies meet regulatory standards for safety and efficacy is critical. Biomedical engineers must navigate complex regulatory processes and conduct rigorous testing to ensure their products are safe for use.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Biomedical engineering involves sensitive data, including genetic and health information. Addressing ethical concerns and ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is essential for maintaining trust and integrity in the field.
Cost and Accessibility
The development of advanced medical technologies can be costly, and ensuring that these innovations are accessible to all patients, regardless of socioeconomic status, is an ongoing challenge.
Future Trends in BME
The field of BME is continuously evolving, with several emerging trends shaping its future:
Personalized Medicine
It is contributing to the advancement of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual patients based on their genetic and biological profiles. This approach aims to enhance treatment effectiveness and minimize adverse effects.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy and tissue engineering, is a growing area within BME. Researchers are working on developing new techniques for repairing and regenerating damaged tissues and organs.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into biomedical engineering. These technologies offer the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, optimize treatment plans, and accelerate drug discovery.
Wearable and Remote Health Monitoring
Wearable devices and remote health monitoring technologies are transforming healthcare by providing continuous data on patients’ health. These innovations enable proactive management of chronic conditions and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Biomedical engineering represents a transformative field at the intersection of medicine and technology. By leveraging engineering principles and innovations, biomedical engineers are developing advanced medical devices, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic solutions that significantly impact patient care. As the field continues to evolve, it holds the promise of further advancements in healthcare, offering new opportunities for improving health and well-being.









