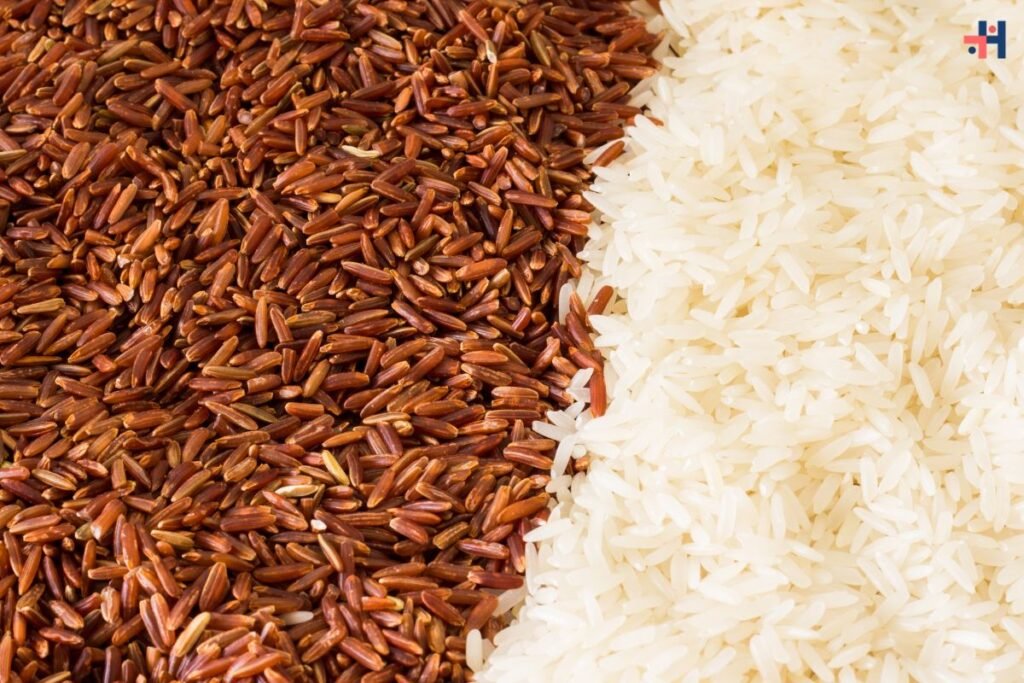
In the realm of dietary choices, the debate between Brown Rice vs. White Rice has sparked considerable interest among health-conscious individuals and nutrition experts alike. Each variety brings its own set of nutritional benefits and considerations to the table, influencing decisions based on health goals, taste preferences, and culinary applications. Let’s explore the differences between Brown Rice vs. White Rice comprehensively to help you make informed choices about incorporating these grains into your diet.
Understanding Brown Rice vs. White Rice
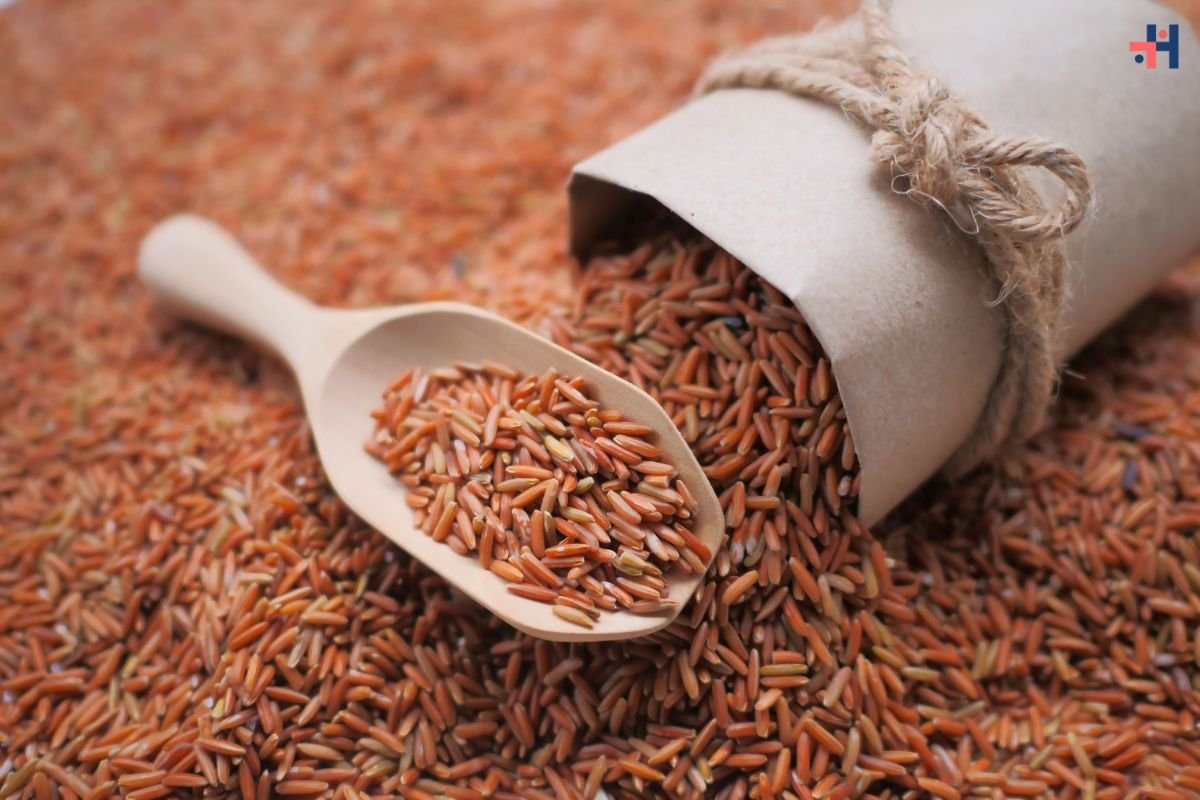
Brown Rice: Embracing Nutrient Density
Brown rice, revered for its intact bran layer and germ, stands out as a nutrient powerhouse compared to its refined counterpart, white rice. This whole grain retains its natural fiber content, essential vitamins (such as B-complex vitamins like B1, B3, and B6), minerals (including magnesium, phosphorus, and selenium), and antioxidants. The fiber in brown rice supports digestive health, regulates blood sugar levels, and promotes a feeling of fullness, making it a preferred choice for those aiming to manage weight and improve overall well-being.
White Rice: Refined Simplicity
White rice undergoes milling and polishing processes that strip away the bran and germ layers, resulting in a grain with a milder flavor and softer texture. While this refining process reduces the fiber content and removes some of the vitamins and minerals found in brown rice, white rice remains a staple in global cuisines for its versatility and quick-cooking properties. It serves as a rapid source of energy due to its easily digestible starch content, making it suitable for individuals needing quick bursts of energy, such as athletes or those recovering from illnesses.
Nutritional Comparison: Brown Rice vs. White Rice

Fiber Content:
- Brown rice contains significantly higher fiber content compared to white rice, which is beneficial for digestive health and satiety.
Vitamins and Minerals:
- Brown rice is richer in vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, magnesium, and selenium, due to its less processed nature.
- White rice, while lower in these nutrients post-processing, may be enriched with vitamins such as folate and iron to compensate for some nutrient loss.
Glycemic Index:
- Brown rice typically has a lower glycemic index compared to white rice, meaning it has a slower effect on blood sugar levels, which can be advantageous for those managing diabetes or seeking stable energy release.
Health Benefits of Brown Rice vs. White Rice
Brown Rice:
- Heart Health: The fiber and nutrients in brown rice contribute to heart health by reducing cholesterol levels and supporting overall cardiovascular function.
- Weight Management: Its higher fiber content aids in weight management by promoting fullness and reducing overall calorie intake.
White Rice:
- Quick Energy: Provides quick energy due to its easily digestible starch, making it suitable for athletes or individuals needing rapid energy replenishment.
- Gentle on Digestion: Its gentle nature makes it suitable for individuals with digestive sensitivities or recovering from gastrointestinal issues.
Culinary Uses and Applications
Both Brown Rice vs. White Rice offer versatility in cooking and can be incorporated into a variety of dishes:
- Brown rice adds a nutty flavor and chewy texture to dishes such as pilafs, stir-fries, and salads.
- White rice serves as a neutral base for dishes worldwide, from sushi and risottos to side dishes paired with meats, vegetables, and sauces.
Making Informed Dietary Choices
When choosing between Brown Rice vs. White Rice, consider your dietary goals, health needs, and personal preferences:
- Nutrient Density: Opt for brown rice for its higher fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidant content.
- Quick Energy: Choose white rice for its quick energy release and ease of digestion.
Exploring the Culinary and Cultural Significance of Brown Rice vs. White Rice
Beyond their nutritional profiles, Brown Rice vs. White Rice hold cultural and culinary significance that adds depth to their popularity worldwide. These grains have been integral parts of traditional diets across various cultures, influencing cooking methods, flavors, and even societal practices. Let’s delve deeper into how Brown Rice vs. White Rice are embraced in different cuisines and their impact on culinary traditions.
Brown Rice: A Staple in Traditional and Health-Conscious Cuisines
Brown rice has long been cherished in cultures where whole grains are valued for their nutritional richness and wholesome flavor. In Asian cuisines, for example, brown rice often accompanies hearty dishes like stir-fries and curries, adding a nutty texture and robustness that complements savory flavors. Its fiber content and slow-digesting properties make it a favored choice among health-conscious individuals aiming to maintain stable blood sugar levels and support digestive health.
In Western cultures, the trend towards whole foods and natural ingredients has further boosted the popularity of brown rice. It is frequently incorporated into salads, pilafs, and grain bowls, offering a satisfying chewiness and earthy taste that enhances the overall dining experience. The rise of plant-based diets and wellness movements has also contributed to brown rice‘s resurgence as a preferred alternative to refined grains.
White Rice: Versatility and Global Appeal
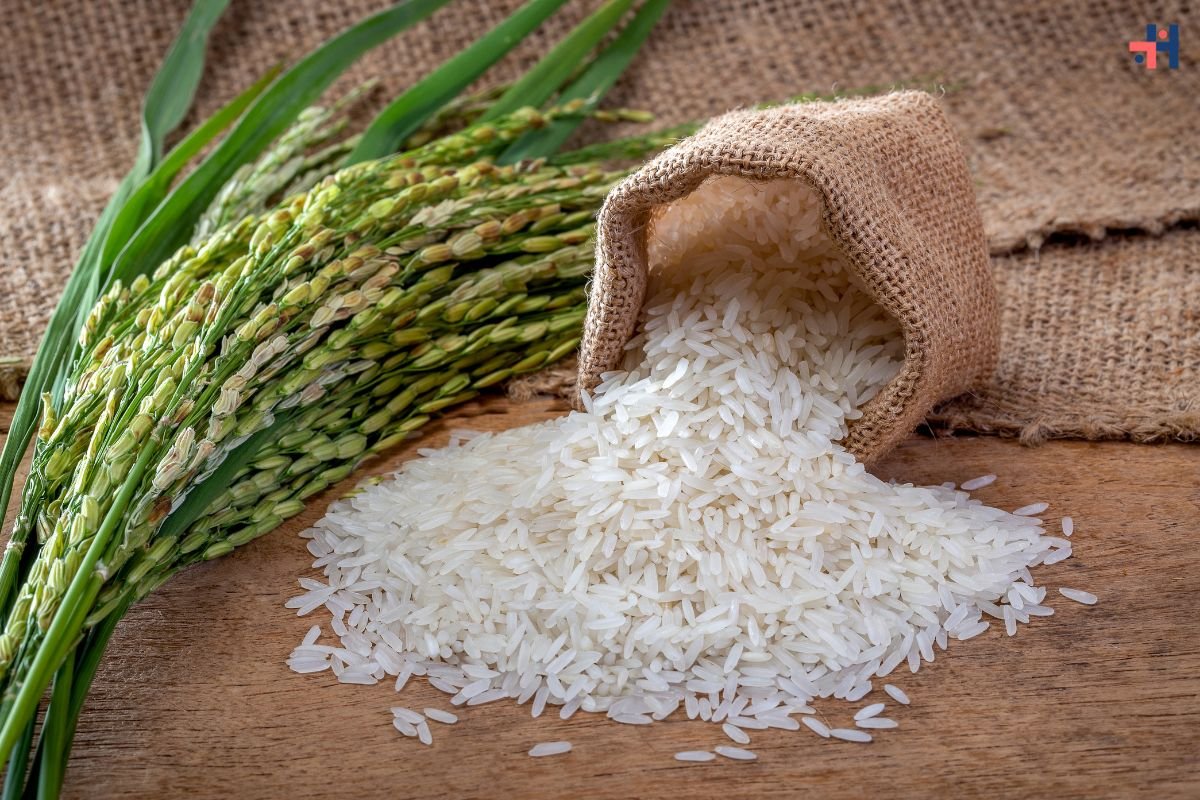

White rice, on the other hand, holds a special place in global cuisines for its versatility, mild flavor, and quick-cooking nature. In many Asian countries such as Japan, China, and Thailand, white rice serves as a staple accompaniment to flavorful dishes like sushi, stir-fries, and curries. Its neutral taste allows it to absorb and complement the flavors of accompanying dishes, making it an indispensable component of everyday meals and festive celebrations alike.
Across Latin America and the Caribbean, white rice plays a central role in traditional dishes such as arroz con pollo (rice with chicken) and rice and beans, showcasing its adaptability to various cooking techniques and regional flavors. Its popularity stems from its ability to provide a filling base that balances spicy, tangy, or savory sauces and proteins, creating comforting and satisfying meals.
Nutritional Considerations and Dietary Preferences
When making dietary choices between Brown Rice vs. White Rice, understanding their nutritional differences is crucial:
- Brown rice offers higher fiber content, vitamins (B-complex vitamins, minerals such as magnesium and phosphorus), and antioxidants, making it beneficial for digestive health, weight management, and overall well-being.
- White rice, while lower in fiber and some nutrients due to processing, remains a valuable source of quick energy and is gentle on the digestive system, making it suitable for individuals with specific dietary needs or preferences.
Integration into Modern Diets and Wellness Trends
As dietary preferences evolve and wellness trends gain momentum, both Brown Rice vs. White Rice continue to adapt to modern lifestyles:
- Brown rice is increasingly embraced for its role in plant-based diets, gluten-free alternatives, and sustainable eating practices, aligning with growing consumer demands for nutritious and environmentally friendly food choices.
- White rice, with its convenience and culinary adaptability, remains a pantry staple in households worldwide, catering to diverse tastes and culinary traditions.
Conclusion: Balancing Nutrition and Preference
In conclusion, the debate between Brown Rice vs. White Rice ultimately boils down to individual dietary preferences, health objectives, and culinary applications. While brown rice shines for its nutrient density and health benefits, white rice offers simplicity, versatility, and rapid energy. Incorporating both varieties into a balanced diet ensures a diverse intake of nutrients and flavors, catering to different nutritional needs and taste preferences. Whether you’re prioritizing fiber intake, managing blood sugar levels, or seeking quick energy, Brown Rice vs. White Rice each have their place in a well-rounded diet. Embrace the diversity of grains and enjoy exploring their culinary possibilities while supporting your health and well-being.