A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights a concerning uptick in severe “flesh-eating” infections in three East Coast states following the unprecedented heat waves of the summer of 2023.
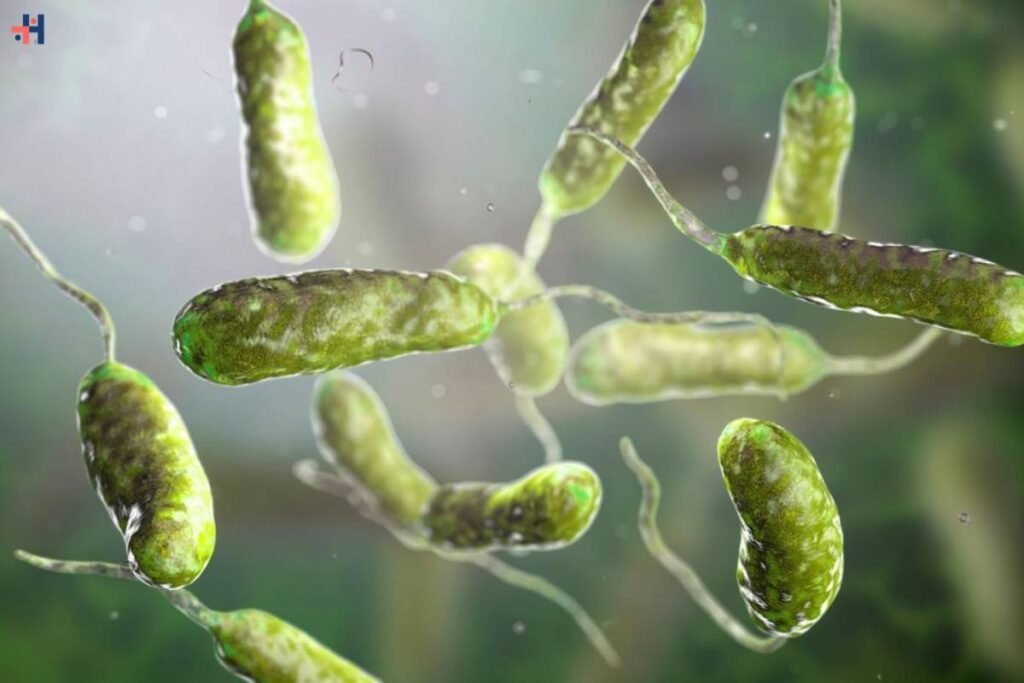
Vibrio vulnificus, a Deadly Culprit
The focus of the report revolves around Vibrio vulnificus, a lethal bacterial species thriving in coastal waters. The microbe, notorious for causing necrotizing fasciitis, can lead to a severe, inflamed infection resulting in rapid tissue death if it enters an open wound. Additionally, when ingested through raw or undercooked seafood, V. vulnificus can trigger gastrointestinal infections, leading to symptoms ranging from watery diarrhea and vomiting to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, published on February 1, delves into the link between the surge in V. vulnificus infections and the environmental conditions prevalent during the summer of 2023. With heat waves and elevated sea surface temperatures occurring between June and August, Connecticut, New York, and North Carolina reported notable cases of severe infections during July and August.
The report emphasizes that while the cases cannot be solely attributed to the heat waves, the well-documented connection between Vibrio bacteria, including V. vulnificus, and environmental conditions conducive to microbial growth raises concerns.
Case Analysis and Preventive Measures
Examining 11 cases of V. vulnificus infection, the affected individuals ranged from 37 to 84 years old, with seven cases reported in North Carolina, two in Connecticut, and two in New York. Tragically, five patients succumbed to the infection, including three who experienced septic shock. The report identifies potential exposure sources, with six cases linked to marine or estuarine water along the U.S. Atlantic coast and two cases resulting from handling raw seafood.
Expected Increase in V. vulnificus Infections as Coastal Water Temperature Rises
The report concludes by highlighting the expected increase in V. vulnificus infections as coastal water temperatures rise. It underscores preventive measures individuals can take, such as avoiding contact between wounds and brackish water, saltwater, and raw seafood. Thoroughly cooking oysters and seafood is also emphasized as a crucial step in preventing infections caused by this dangerous bacterium.
As the world grapples with the complex intersection of climate change and public health, this report serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences, urging vigilance and proactive measures to mitigate the risk of severe infections tied to environmental fluctuations.
Also Read: Embracing a Plant-Based Diet for a Sustainable Tomorrow