(Source-CBS-News)
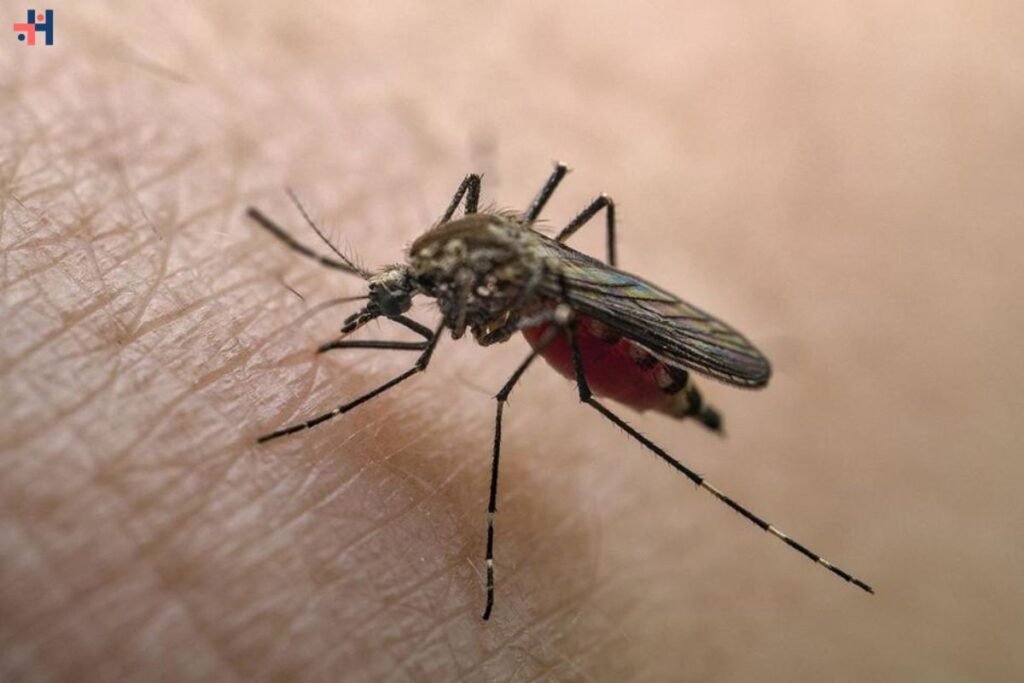
Federal health officials have issued a nationwide alert concerning the rapid spread of dengue fever, a mosquito-borne virus infection that has seen a threefold increase in cases compared to the previous year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported a significant rise in cases primarily linked to travel abroad, where dengue fever is endemic and spreading swiftly. Currently, the only state with confirmed cases of local transmission is Florida, though U.S. territories such as Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands are also experiencing localized outbreaks of the disease.
Geographic Distribution and Impact
As of the latest CDC data, dengue fever cases have been confirmed in 38 states and the District of Columbia this year. A detailed map highlights the extent of the outbreak across the country: states shaded in gray indicate no reported cases, pale green signifies one to four cases, teal represents five to 49 cases, and blue denotes states with between 49 to 250 confirmed cases of dengue fever. Florida leads with 191 cases, followed by New York with 134 cases and Massachusetts with 50 cases. Nationwide, over 2,241 cases have been documented, prompting health authorities to advise vigilance among healthcare providers.
Global Trends and Health Concerns
Globally, the surge in dengue fever cases remains a pressing issue, with over 7.9 million cases reported worldwide in the first four months of the year, resulting in approximately 4,000 deaths. The World Health Organization (WHO) notes a particularly intense outbreak in the Americas, affecting countries like Brazil and Peru. Dengue fever typically manifests with flu-like symptoms such as fever, nausea, vomiting, joint pain, and headaches, appearing five to seven days post-infection. Severe cases can lead to life-threatening complications such as severe bleeding and shock, with no widely available treatment currently available for the infection.
Health experts attribute the escalating prevalence of dengue fever to the expanding range of mosquito-borne virus that carry the virus, facilitated by warming climates due to climate change. In response to the growing threat, the CDC has advised healthcare professionals to familiarize themselves with dengue symptoms, inquire about recent travel history when evaluating patients, and consider ordering dengue tests as part of diagnostic protocols.
As dengue fever continues to pose a significant health risk both domestically and globally, heightened awareness and proactive measures are crucial in curbing its spread and mitigating its impact on public health.