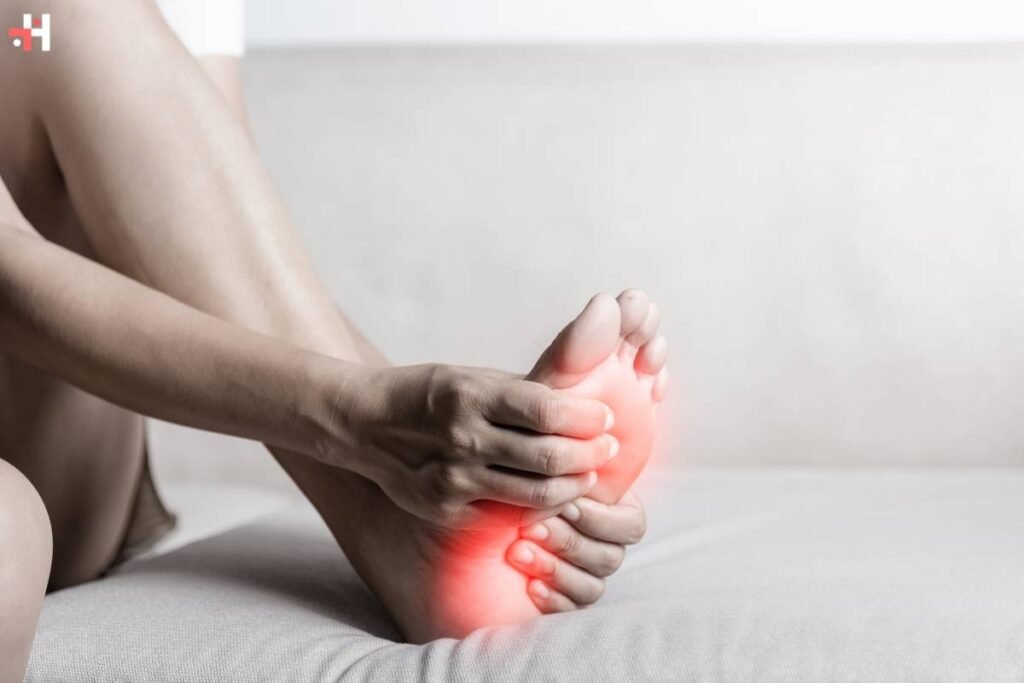
For people with diabetes, it’s critical to manage a number of health issues. Diabetes can lead to a number of complications, with foot problems being particularly common. Symptoms of diabetic foot discomfort may indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed. We will examine the many diabetic foot pain symptoms and signs, as well as possible causes and crucial management and preventative techniques, in this in-depth guide.
Here are 15 common diabetic foot pain symptoms:
1. Numbness and Tingling: Early Signs of Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic foot pain symptoms often begin with sensations of numbness and tingling. Peripheral neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, affects the nerves in the extremities, including the feet. As nerve damage progresses, individuals may experience a loss of sensation, making it difficult to detect injuries or changes in temperature. Regular foot checks become crucial for preventing complications that may arise due to unnoticed injuries.
2. Burning Sensation: Neuropathic Pain in Diabetic Feet
As diabetic neuropathy advances, some individuals may experience a persistent burning sensation in their feet. This neuropathic pain can range from mild discomfort to more intense sensations, impacting the overall quality of life. Addressing this symptom promptly is essential, as ongoing neuropathic pain may lead to sleep disturbances and decreased mobility.
3. Changes in Skin Texture: Dryness and Cracking
Diabetes can affect the skin on the feet, leading to changes in texture. Dry and cracked skin is a common diabetic foot pain symptoms. Reduced moisture in the skin can make it more prone to cracking, which, if left untreated, may evolve into open sores. Regular moisturization and proper foot care are vital to prevent complications associated with dry and cracked skin.
4. Foot Ulcers: Serious Complications Requiring Immediate Attention
Foot ulcers are one of the most severe diabetic foot pain symptoms, often resulting from a combination of neuropathy and vascular issues. Reduced blood flow to the extremities, common in diabetes, can slow down the healing process. Even minor injuries, such as blisters or cuts, can develop into ulcers if not treated promptly. Diabetic foot ulcers pose a significant risk of infection, and in severe cases, may lead to amputation if left unaddressed.
5. Changes in Nail Health: Thickened or Discolored Nails
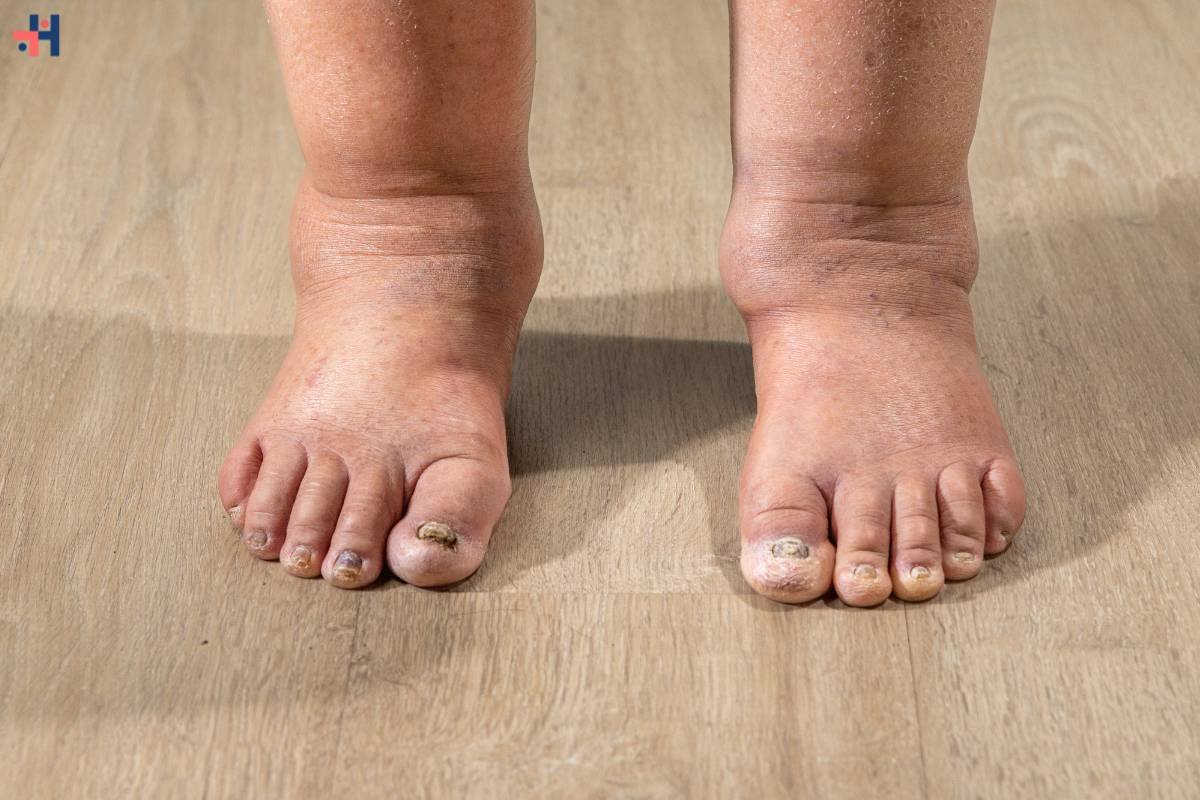
Diabetes can also impact the health of the nails on the feet. Changes such as thickened or discolored nails may indicate fungal infections, another common concern for individuals with diabetes. Fungal infections can thrive in the warm and moist environment inside shoes, making regular nail care and hygiene crucial for preventing complications.
6. Foot Deformities: Structural Changes Over Time
Long-term uncontrolled diabetes can lead to structural changes in the feet, resulting in deformities. Conditions such as Charcot foot, a progressive degeneration of the bones and joints in the feet, can cause noticeable changes in foot structure. Swelling, instability, and changes in foot shape are characteristic symptoms of Charcot foot, requiring immediate medical attention to prevent further complications.
7. Painful Cramps: Muscular Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy can also affect the muscles in the feet, leading to painful cramps. These cramps may occur spontaneously and cause discomfort, affecting mobility and overall well-being. Proper glycemic control and lifestyle modifications may help alleviate muscular symptoms associated with diabetic neuropathy.
8. Decreased Wound Healing: Prolonged Recovery Time
Diabetes can impact the body’s ability to heal effectively. Even minor wounds, cuts, or abrasions on the feet may take longer to heal in individuals with diabetes. Delayed wound healing increases the risk of infection, emphasizing the importance of vigilant foot care and prompt attention to any injuries.
9. Peripheral Arterial Disease: Impaired Blood Flow to the Feet
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a vascular complication commonly associated with diabetes. Reduced blood flow to the extremities, particularly the feet, can result in symptoms such as cramping, numbness, and pain. Individuals with diabetes should be vigilant about assessing blood flow to their feet and promptly report any changes to their healthcare provider.
10. Redness and Swelling: Signs of Infection
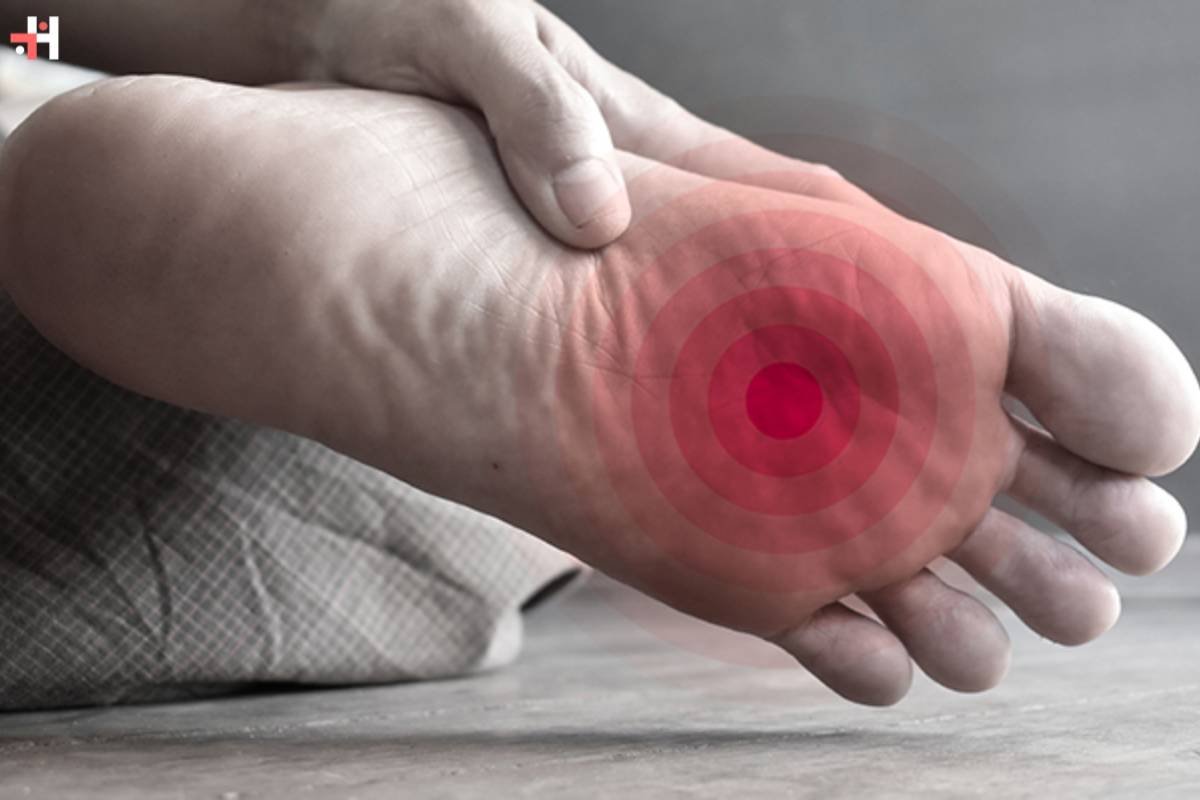
Redness and swelling in the feet may indicate the presence of an infection, which can be more challenging to combat in individuals with diabetes. Poor circulation, impaired immune function, and nerve damage contribute to an increased risk of infections. Any signs of redness, warmth, or swelling should be promptly addressed to prevent the spread of infection.
11. Cold Feet: Poor Circulation Warning Signs
Diabetic foot pain symptoms may also manifest as a persistent sensation of cold feet. Reduced blood flow to the extremities can result in poor circulation, leading to a perpetual feeling of coldness. Cold feet may be an early warning sign of vascular issues and should be investigated by a healthcare professional.
12. Joint Pain and Stiffness: Arthritic Changes
Diabetes can contribute to arthritic changes in the joints of the feet, leading to pain and stiffness. Individuals may experience difficulty with joint mobility, affecting their ability to walk comfortably. Proper foot care, including appropriate footwear and regular monitoring, is essential to manage arthritic symptoms associated with diabetes.
13. Foot Discoloration: Indicators of Vascular Complications
Changes in the color of the feet, such as a bluish or purplish hue, can signal vascular complications. Reduced blood flow may result in poor oxygenation of the tissues, leading to discoloration. Addressing vascular concerns is crucial for preventing further complications and promoting overall foot health.
14. Foot Swelling: Fluid Accumulation and Poor Circulation
Swelling in the feet, also known as edema, can occur due to poor circulation and fluid retention. Individuals with diabetes should be vigilant about any signs of swelling, as it may indicate underlying vascular issues. Elevation of the feet, compression stockings, and lifestyle modifications may help manage swelling associated with diabetic foot pain symptoms.
15. Gangrene: Advanced Stage Complications Requiring Urgent Intervention
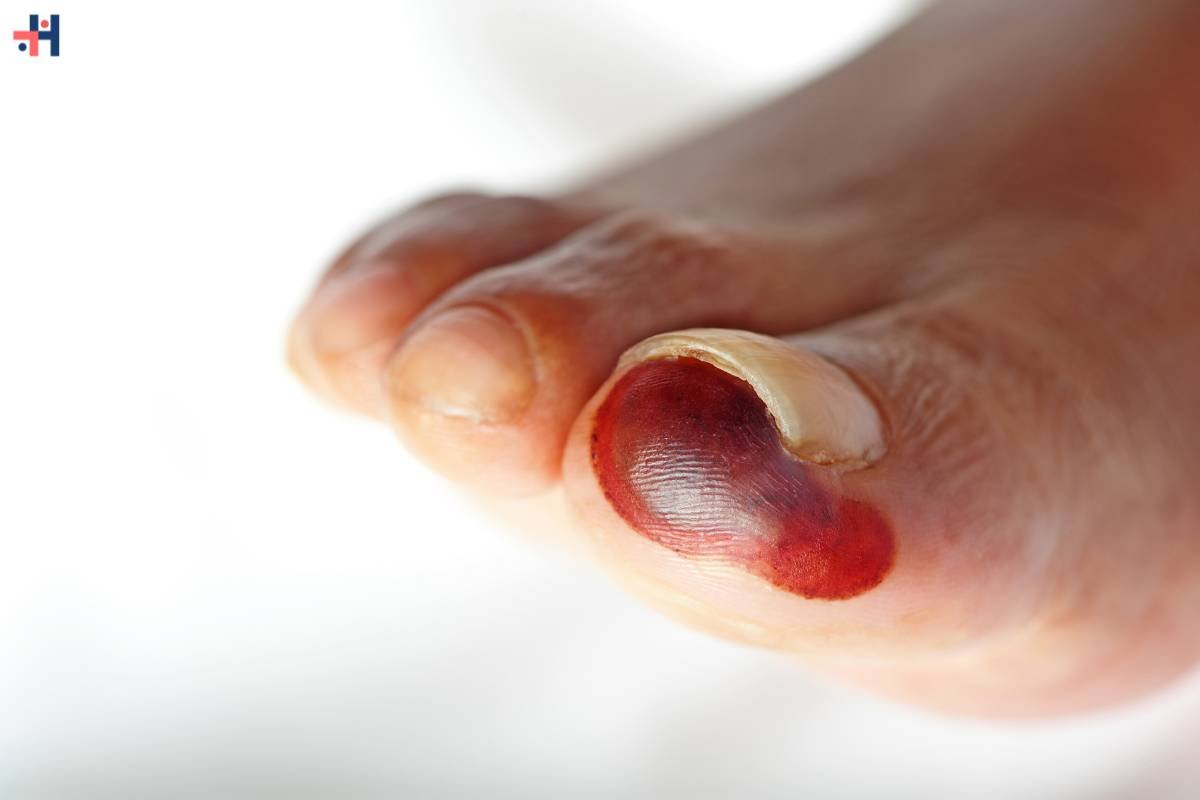
In severe cases, untreated diabetic foot pain symptoms can progress to gangrene, a condition characterized by tissue death. Gangrene is a medical emergency and requires immediate intervention. Symptoms include darkening of the skin, foul odor, and the presence of open sores or wounds. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent the spread of gangrene and preserve as much healthy tissue as possible.
Conclusion:
For those who have diabetes, it is critical to comprehend and identify the signs of diabetic foot pain. The management of diabetes requires regular foot care, regular check-ups, and quick reaction to any changes or discomfort. Diabetes patients can reduce the chance of problems and preserve ideal foot health by being watchful and treating symptoms as soon as they arise. Getting advice from medical experts, such as diabetic specialists and podiatrists, is essential to creating a customized care plan that meets each patient’s needs. Diabetics can prioritise their overall well-being and control the symptoms of diabetic foot discomfort with proactive treatment and dedication to foot care.