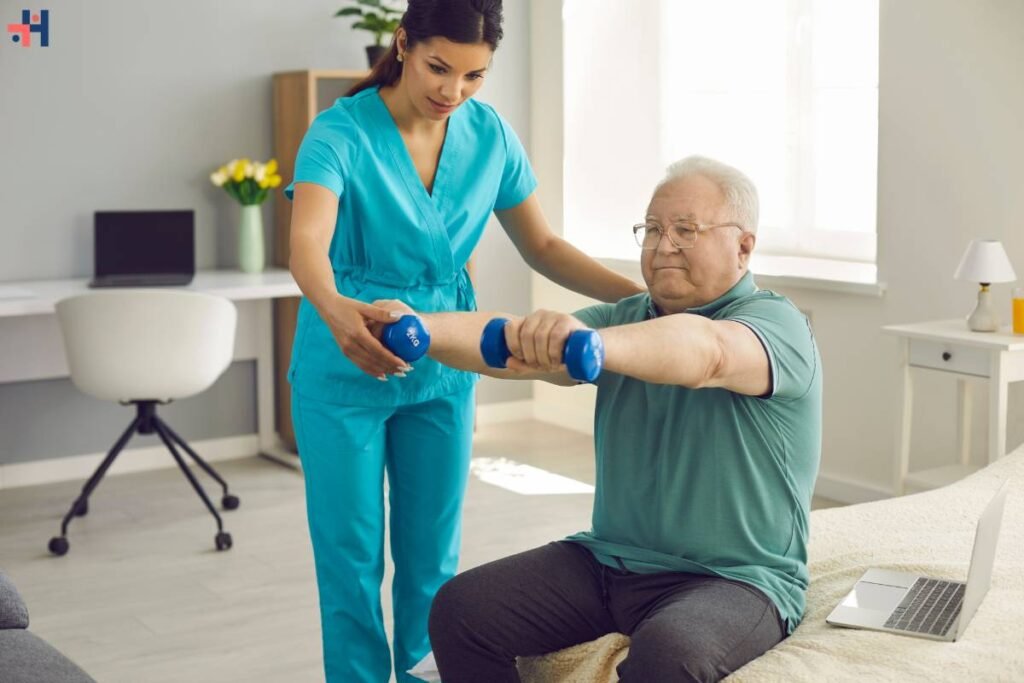
Orthopedic rehabilitation is a vital component of healthcare aimed at restoring function, mobility, and quality of life for individuals recovering from musculoskeletal injuries, surgeries, or conditions. Through a combination of specialized techniques, therapeutic modalities, and personalized treatment plans, orthopedic rehabilitation addresses the unique needs of each patient and facilitates optimal recovery outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deeper into the techniques, benefits, and journey of recovery in orthopedic rehabilitation.
Benefits of Orthopedic Rehabilitation:
1. Enhanced Musculoskeletal Function:
Orthopedic rehabilitation focuses on strengthening muscles, improving joint mobility, and enhancing overall musculoskeletal function. Through targeted exercises and interventions, individuals can regain stability, coordination, and motor control, allowing them to perform daily activities with greater ease and confidence.
2. Pain Management and Symptom Relief:
Orthopedic injuries and conditions often cause pain, discomfort, and inflammation. Rehabilitation programs incorporate pain management strategies such as manual therapy, modalities, and therapeutic exercises to alleviate symptoms, reduce reliance on pain medications, and promote natural healing processes.
3. Prevention of Secondary Complications:
Orthopedic rehabilitation helps prevent secondary complications associated with musculoskeletal injuries or surgeries. By addressing muscle imbalances, postural abnormalities, and movement dysfunctions, rehabilitation programs reduce the risk of chronic pain, joint stiffness, and functional limitations in the long term.
4. Improved Quality of Life:

Through improved mobility, function, and pain relief, orthopedic rehabilitation enhances the overall quality of life for individuals recovering from orthopedic conditions. By restoring independence and autonomy, rehabilitation empowers patients to engage in meaningful activities, pursue hobbies, and participate in social interactions with confidence.
5. Optimized Surgical Outcomes:
For individuals undergoing orthopedic surgeries such as joint replacement or ligament repair, pre-operative and post-operative rehabilitation plays a crucial role in optimizing surgical outcomes. Rehabilitation programs help prepare patients for surgery, expedite post-operative recovery, and facilitate a smoother transition back to functional activities.
Techniques and Modalities in Orthopedic Rehabilitation:
1. Therapeutic Exercises:
Physical therapists design individualized exercise programs tailored to each patient’s specific needs and goals. These exercises may include strength training, flexibility exercises, balance training, proprioceptive exercises, and functional movements aimed at improving overall musculoskeletal function and mobility.
2. Manual Therapy:
Hands-on techniques performed by skilled therapists, such as joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, and myofascial release, help alleviate pain, reduce muscle tension, and improve joint mobility. Manual therapy techniques are often integrated into rehabilitation programs to complement exercise-based interventions and enhance overall outcomes.
3. Modalities:
Various therapeutic modalities are utilized in orthopedic rehabilitation to manage pain, inflammation, and promote tissue healing. Common modalities include heat therapy, cold therapy, ultrasound, electrical stimulation (e.g., TENS), laser therapy, and hydrotherapy. These modalities can be used adjunctively to enhance the effectiveness of other treatment modalities.
4. Functional Rehabilitation:
Functional rehabilitation focuses on restoring movement patterns and activities of daily living that are essential for functional independence. Through task-specific training, functional exercises, and activity modifications, individuals learn to perform everyday tasks with greater efficiency and confidence, reducing the risk of re-injury and promoting long-term functional independence.
5. Biomechanical Analysis:

Biomechanical analysis involves the assessment of movement patterns, joint mechanics, and musculoskeletal alignment to identify underlying dysfunctions and imbalances. By addressing biomechanical issues, therapists can develop targeted interventions to improve movement efficiency, reduce stress on injured tissues, and prevent future injuries.
6. Patient Education and Lifestyle Modification:
Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, treatment strategies, and self-care practices is integral to the rehabilitation process. Therapists educate patients on proper body mechanics, ergonomic principles, injury prevention strategies, and lifestyle modifications to support long-term musculoskeletal health and prevent re-injury.
Also Read: The Power of Physical Therapy in Rehabilitation
Recovery and Rehabilitation Journey:
1. Initial Evaluation and Assessment:
The rehabilitation journey begins with a comprehensive evaluation conducted by a qualified healthcare professional, typically a physical therapist or orthopedic specialist. During the assessment, the therapist gathers information about the patient’s medical history, functional limitations, goals, and preferences to develop a personalized treatment plan.
2. Goal Setting and Treatment Planning:
Collaboratively with the patient, the therapist establishes realistic and achievable goals that address the individual’s functional needs and objectives. Based on the assessment findings, the therapist designs a customized treatment plan incorporating various techniques, modalities, and interventions to address specific impairments and promote optimal recovery.
3. Progressive Rehabilitation:
Rehabilitation is a dynamic process that evolves over time as the patient’s condition improves. The therapist progressively advances the intensity, duration, and complexity of exercises and interventions to challenge the patient’s abilities while ensuring safety and efficacy. Regular re-evaluations are conducted to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
4. Functional Training and Return to Activity:
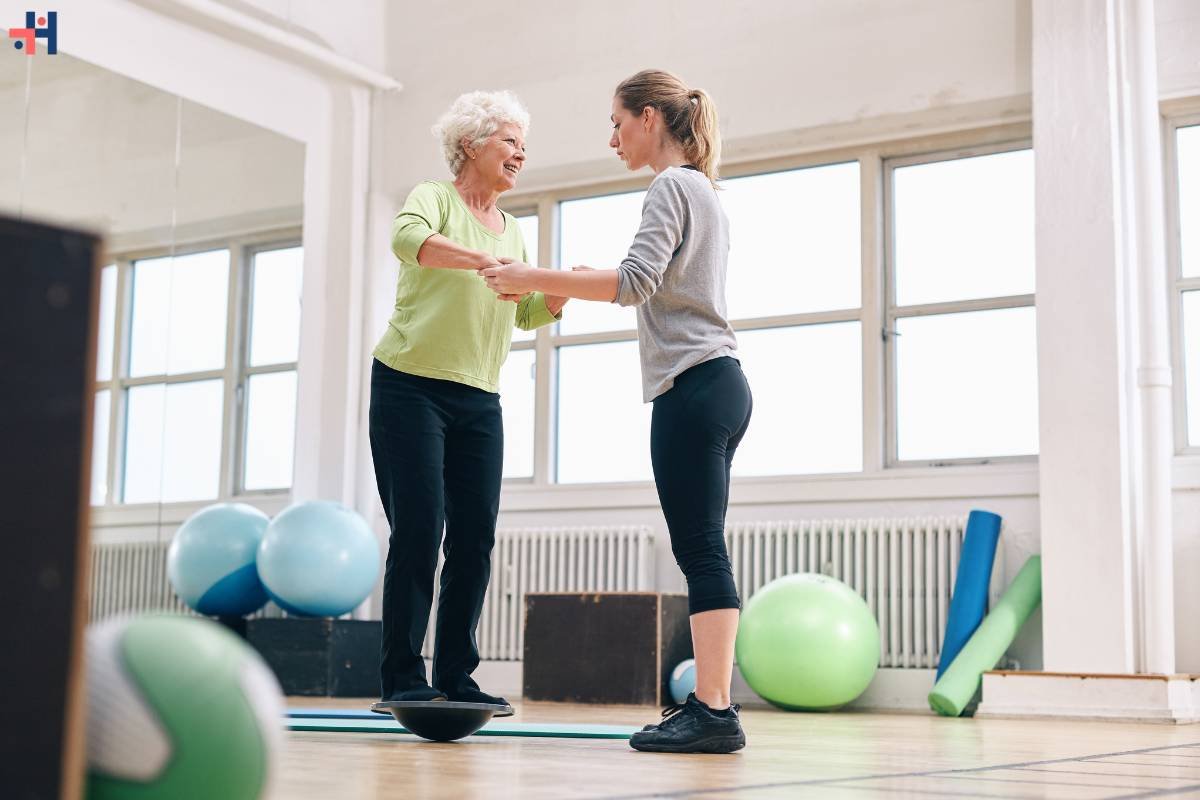

As the patient progresses through rehabilitation, emphasis is placed on functional training and activities of daily living. Therapists simulate real-life scenarios and tasks to help patients regain confidence, independence, and functional capacity in their daily lives, work, and recreational activities.
5. Transition to Home Exercise Program:
Upon completion of formal rehabilitation sessions, patients are provided with a home exercise program tailored to their needs and goals. The home exercise program serves as a continuation of the rehabilitation process, allowing patients to maintain gains, prevent regression, and further improve musculoskeletal function and mobility.
6. Long-Term Follow-Up and Maintenance:
Following the completion of orthopedic rehabilitation, patients are encouraged to continue with long-term follow-up care and maintenance exercises to support ongoing recovery and musculoskeletal health. Regular physical activity, proper nutrition, and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in maintaining optimal function and preventing re-injury in the long term.
Conclusion:
Orthopedic rehabilitation encompasses a comprehensive approach to restoring function, mobility, and quality of life for individuals recovering from musculoskeletal injuries, surgeries, or conditions. Through a combination of specialized techniques, therapeutic modalities, and personalized treatment plans, rehabilitation programs address the unique needs of each patient and facilitate optimal recovery outcomes. By empowering patients with knowledge, skills, and strategies for self-care, orthopedic rehabilitation promotes long-term musculoskeletal health, functional independence, and overall well-being