In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, the integration of technology has become paramount in improving patient care, streamlining operations, and advancing medical research. Health Information Technology (HIT) stands at the forefront of this transformation, offering innovative solutions to enhance the delivery and management of healthcare services. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of Health Information Technology, exploring its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Health Information Technology:
Health Information Technology refers to the use of digital systems to manage and exchange health information securely. These systems encompass a wide range of technologies, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), telemedicine platforms, health information exchanges (HIEs), patient portals, and mobile health applications. The primary goal of HIT is to improve the quality, efficiency, and safety of healthcare delivery by enabling seamless communication and data exchange among healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders.
Benefits of Health Information Technology:
1. Enhanced Patient Care:
EHRs facilitate comprehensive and accessible patient records, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions and deliver personalized care.
Telemedicine platforms enable remote consultations, improving access to healthcare services, especially for underserved populations and rural areas.
Clinical decision support systems help healthcare professionals in diagnosing conditions, selecting appropriate treatments, and preventing medical errors.
2. Improved Coordination and Communication:

HIEs allow healthcare organizations to share patient information securely, facilitating care coordination across different providers and settings.
Secure messaging platforms and patient portals enable effective communication between patients and healthcare providers, promoting engagement and collaboration in care management.
3. Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
Automated workflows and electronic documentation streamline administrative tasks, reducing paperwork and freeing up healthcare professionals’ time to focus on patient care.
Integration with other healthcare systems and interoperability standards enable seamless data exchange, eliminating redundancies and improving workflow efficiency.
4. Enhanced Data Analytics and Population Health Management:
Health information technology enables the aggregation and analysis of large volumes of healthcare data, providing valuable insights into population health trends, disease prevalence, and treatment outcomes.
Predictive analytics tools help identify high-risk patients, enabling proactive interventions and preventive care strategies to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Challenges and Barriers:
Despite its numerous benefits, the widespread adoption and implementation of Health Information Technology face several challenges and barriers:
1. Privacy and Security Concerns:
Safeguarding patient privacy and protecting health information from cybersecurity threats remains a significant concern in HIT implementation.
Compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is essential to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of patient data.
2. Interoperability Issues:
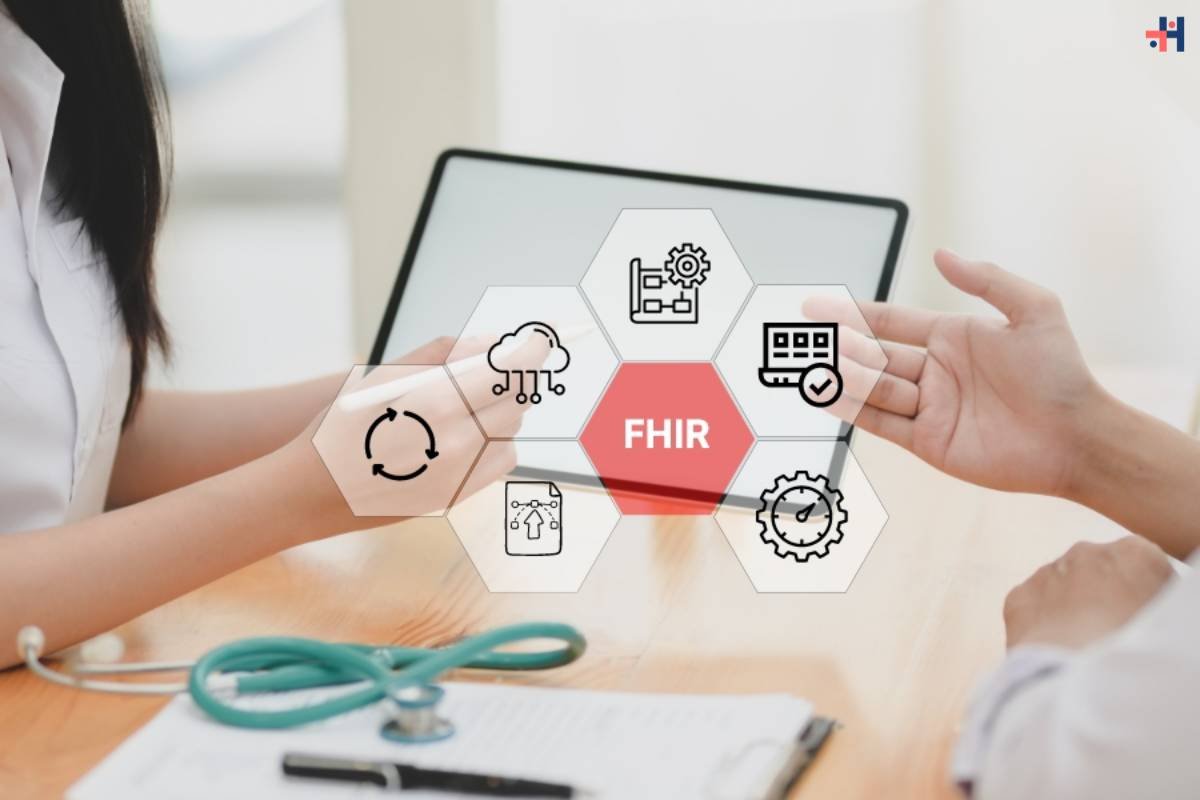

(Source – smartData Enterprises)
The lack of standardized data formats and interoperability among different HIT systems hinders seamless data exchange and interoperability, leading to fragmented care and inefficiencies.
Efforts to promote interoperability through initiatives such as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) are underway, but achieving widespread interoperability remains a challenge.
3. Cost and Resource Constraints:
The initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs associated with implementing and maintaining HIT systems can be prohibitive for smaller healthcare organizations and underserved communities.
Limited access to technical expertise and resources poses challenges in optimizing HIT systems and maximizing their potential benefits.
4. Resistance to Change:
Resistance to change among healthcare professionals and staff members, coupled with workflow disruptions during the transition to HIT systems, can impede adoption and acceptance.
Effective change management strategies, training programs, and stakeholder engagement initiatives are essential to address resistance and foster a culture of innovation and collaboration.
Future Trends and Opportunities:
Despite the challenges, Health Information Technology continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in digital health, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. Some emerging trends and opportunities in HIT include:
1. Adoption of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
- AI-powered tools and algorithms hold promise in enhancing clinical decision-making, predicting disease outcomes, and optimizing treatment strategies.
- Applications of machine learning in healthcare range from diagnostic imaging and predictive analytics to personalized medicine and virtual health assistants.
2. Expansion of Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring:
- The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth and remote monitoring technologies, leading to a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery.
- Telehealth platforms and wearable devices enable real-time monitoring of patients’ vital signs, medication adherence, and disease progression, improving access to care and patient outcomes.
3. Focus on Population Health and Value-based Care:
- Healthcare organizations are increasingly shifting towards value-based care models that prioritize patient outcomes and population health management.
- HIT systems play a crucial role in supporting population health initiatives, data-driven interventions, and preventive care strategies to improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Also Read: Blockchain in Healthcare Data Security: A Revolutionary Frontier
Conclusion:
Health Information Technology has emerged as a transformative force in modern healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient care, enhance efficiency, and advance medical research. By leveraging innovative technologies and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, healthcare organizations can harness the full potential of HIT to address the evolving challenges and opportunities in healthcare delivery. As we continue to embrace digital transformation, the future of healthcare lies at the intersection of technology, data, and patient-centered care.