In the realm of nutrition, few nutrients are as crucial as protein. From building and repairing tissues to supporting immune function and hormone production, protein plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. As awareness about nutrition grows, so does the emphasis on choosing quality protein sources. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the world of protein sources, exploring different types, their benefits, and how to incorporate them into a balanced diet.
Understanding Protein Basics
Before we delve into protein sources, let’s understand the basics. Proteins are made up of amino acids, often referred to as the building blocks of life. There are 20 amino acids, nine of which are essential, meaning the body cannot produce them and must obtain them from food. Proteins are essential for:
- Muscle Growth and Repair: Protein provides the necessary amino acids for muscle tissue repair and growth, making it essential for athletes and anyone engaged in physical activity.
- Enzyme and Hormone Production: Many enzymes and hormones crucial for various bodily functions are made up of proteins.
- Immune Function: Antibodies, critical for immune function, are proteins that help fight infections and diseases.
- Cell Structure: Proteins are essential for maintaining cell structure and integrity.
- Energy Source: While carbohydrates and fats are primary energy sources, proteins can be used for energy when needed.
Different Types of Protein Sources
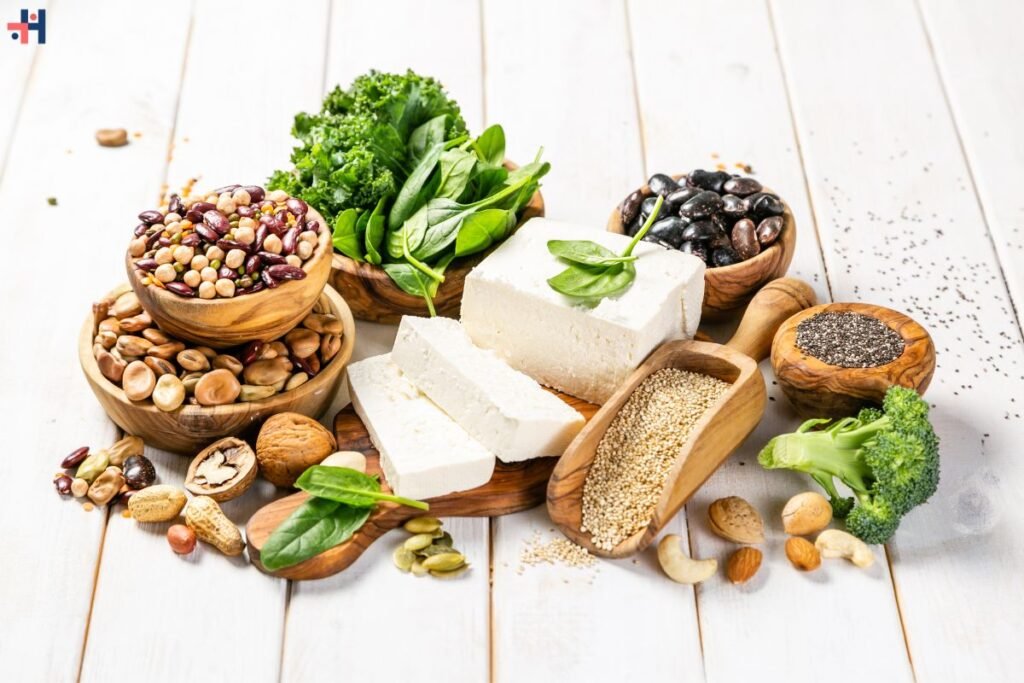
Protein sources can be broadly classified into animal-based and plant-based sources. Each type offers unique benefits and considerations.
Animal-Based Protein Sources
- Lean Meats: Chicken, turkey, lean cuts of beef, and pork are rich sources of high-quality protein. They also provide essential nutrients like iron and B vitamins.
- Fish and Seafood: Salmon, tuna, trout, and shellfish not only provide protein but also omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial for heart health and inflammation reduction.
- Eggs: Egg whites are pure protein, while yolks contain healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals like vitamin D and choline.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are rich in protein, calcium, and other nutrients. Opt for low-fat or fat-free options to reduce saturated fat intake.
Plant-Based Protein Sources

- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of plant-based protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals.
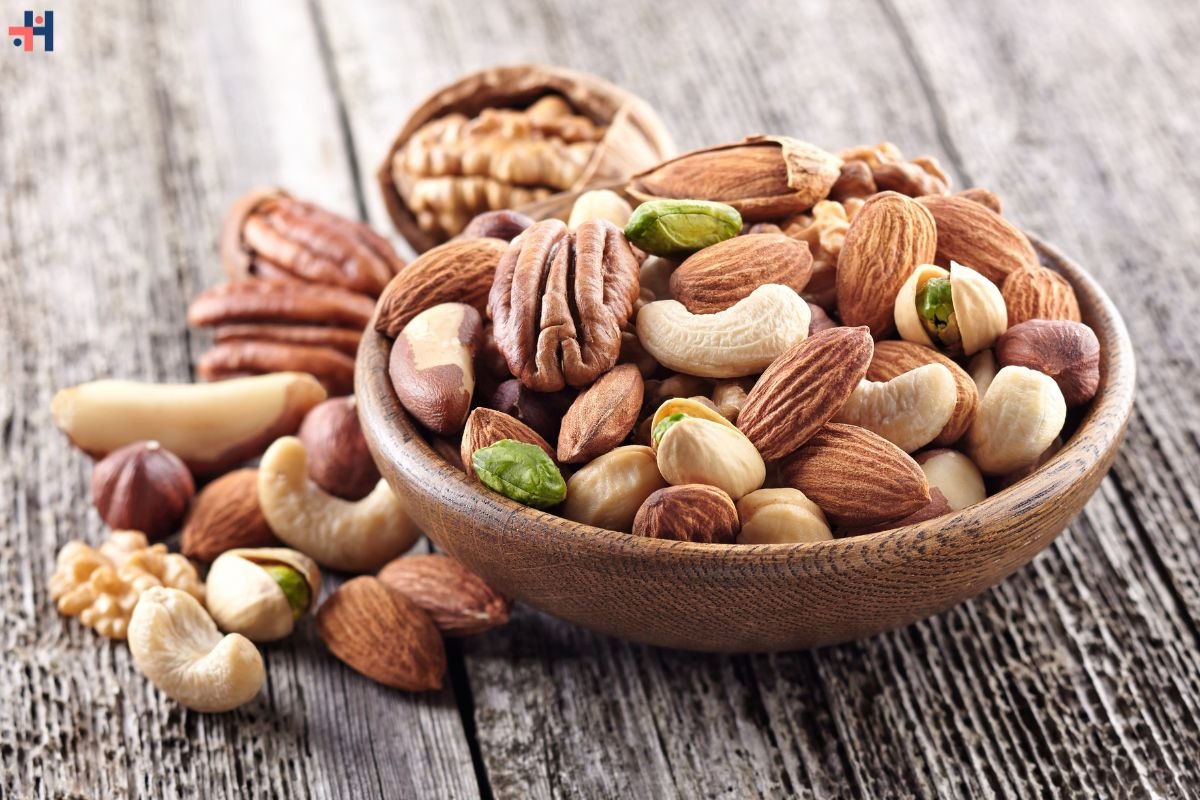
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, peanuts, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds offer protein, healthy fats, and micronutrients like magnesium and zinc.
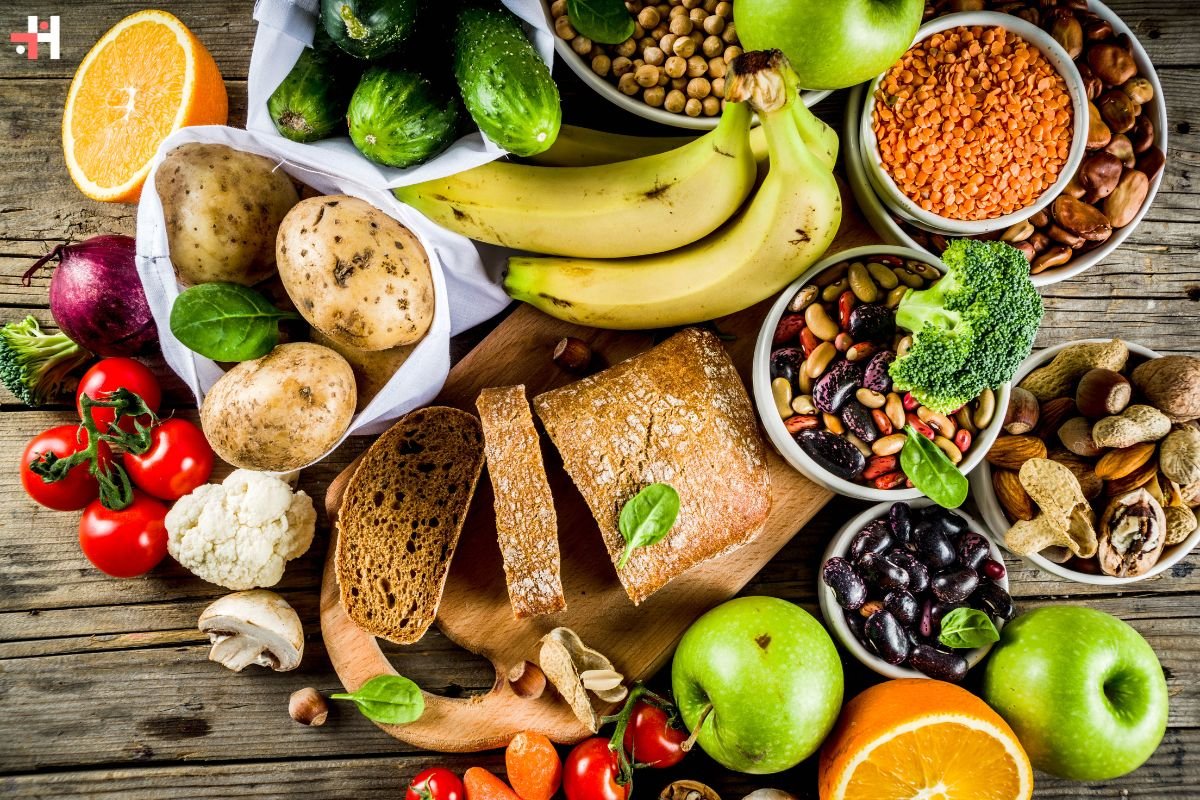
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat products contribute protein along with fiber and complex carbohydrates.
- Soy Products: Tofu, tempeh, and edamame are complete protein sources, containing all essential amino acids. They are also rich in phytonutrients like isoflavones.
Benefits of Diversifying Protein Sources
- Optimal Nutrient Intake: Different protein sources offer varying nutrient profiles, ensuring a broader intake of vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients.
- Reduced Saturated Fat Intake: Diversifying protein sources allows for a balanced diet with lower saturated fat intake, which is beneficial for heart health.
- Environmental Sustainability: Plant-based proteins generally have a lower environmental impact compared to animal-based proteins, contributing to sustainability efforts.
- Allergen Considerations: For individuals with allergies or intolerances, diversifying protein sources helps avoid dietary limitations while meeting nutritional needs.
Incorporating Protein Sources Into Your Diet
Now that we’ve covered the types and benefits of protein sources, let’s discuss practical ways to incorporate them into your diet:
- Balanced Meals: Include a source of protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats, and vegetables in each meal for a balanced nutrient intake.
- Snack Smart: Opt for protein-rich snacks like Greek yogurt, mixed nuts, hummus with veggies, or a hard-boiled egg for sustained energy levels.
- Meal Prep: Cook large batches of lean meats, legumes, and grains for easy meal assembly throughout the week.
- Smoothies: Blend protein-rich ingredients like spinach, Greek yogurt, protein powder, and fruits for a nutritious and filling smoothie.
- Plant-Based Meals: Incorporate meatless meals using tofu, tempeh, beans, or lentils as the main protein source for variety and health benefits.
Maximizing Protein Absorption

Simply consuming protein isn’t enough; optimizing absorption is key to reaping its benefits fully. Consider these strategies:
- Pair with Fiber: Combine protein-rich foods with fiber-rich options like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains to enhance digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Include Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil to improve the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and promote satiety.
- Hydration: Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to support digestion and nutrient transport, including protein.
- Timing: Distribute protein intake evenly throughout the day, including post-workout to support muscle recovery and growth.
Addressing Common Protein Misconceptions
- More Isn’t Always Better: While protein is crucial, consuming excessive amounts won’t necessarily yield additional benefits and may strain kidney function in some individuals.
- Quality Matters: Focus on quality protein sources like lean meats, legumes, and dairy products rather than heavily processed or fried options.
- Individual Needs Vary: Factors such as age, activity level, and health conditions influence protein requirements. Consult a healthcare provider or nutritionist for personalized recommendations.
- Variety is Key: A diverse diet ensures a range of nutrients beyond just protein, supporting overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Protein is an essential nutrient that plays multifaceted roles in maintaining health and supporting bodily functions. By understanding different protein sources, their benefits, and strategies for optimal intake, you can make informed dietary choices that promote overall wellness. Whether you prefer animal-based or plant-based options, prioritizing quality and variety ensures a balanced diet that fuels your body effectively. Consult with nutrition professionals for personalized guidance, especially if you have specific dietary needs or health goals. Unlock the power of protein sources and unlock the potential for a healthier, more vibrant life.