Dehydration, a condition where the body loses more fluids than it takes in, is a common yet often underestimated health concern among adults. It can range from mild to severe and affects various bodily functions, making it crucial to recognize its signs early. This comprehensive guide explores the signs, symptoms, risk factors, prevention tips, and when to seek medical help for signs of dehydration in adults.
Understanding Dehydration
Water is essential for the body’s optimal functioning, including regulating temperature, aiding digestion, and transporting nutrients. When the body loses more fluids than it consumes, dehydration occurs. Mild dehydration can typically be reversed by increasing fluid intake, while severe cases may require medical intervention to restore balance.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Dehydration in Adults

- Increased Thirst: Feeling unusually thirsty is often the first sign of dehydration. This occurs as the body tries to replenish lost fluids.
- Dry Mouth and Sticky Saliva: Reduced saliva production leads to dryness in the mouth and throat, causing discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
- Reduced Urination: Dark-colored urine or infrequent urination suggests the body is conserving fluids to maintain hydration.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Dehydration can lead to a drop in blood pressure and reduced oxygen delivery to muscles, resulting in fatigue and weakness.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Electrolyte imbalances due to dehydration can affect brain function, causing dizziness or faintness.
- Headaches: Dehydration reduces blood flow and oxygen to the brain, triggering headaches.
- Dry Skin: Inadequate hydration affects skin elasticity and moisture levels, leading to dry, flaky skin.
- Muscle Cramps: Electrolyte imbalances from fluid loss can cause painful muscle cramps, particularly during physical activity.
- Increased Heart Rate: Dehydration reduces blood volume, prompting the heart to work harder to circulate blood, resulting in a faster heartbeat.
- Confusion or Irritability: Severe dehydration can impair cognitive function, causing confusion, irritability, or even delirium.
- Sunken Eyes: Dehydration may cause the eyes to appear sunken due to fluid loss.
- Thirst and Dryness of Mucous Membranes: A persistent sensation of thirst and dryness in the nose and throat can indicate dehydration.
Risk Factors for Signs of Dehydration in Adults
Several factors increase the risk of dehydration in adults:
- Hot Weather: Excessive sweating in high temperatures accelerates fluid loss.
- Intense Physical Activity: Vigorous exercise increases fluid requirements.
- Illnesses: Fever, vomiting, or diarrhea can lead to significant fluid loss.
- Age: Infants, older adults, and individuals with chronic illnesses are more vulnerable to dehydration.
- Certain Medications: Diuretics and medications that induce sweating can contribute to dehydration.
Prevention Tips for Signs of Dehydration in Adults
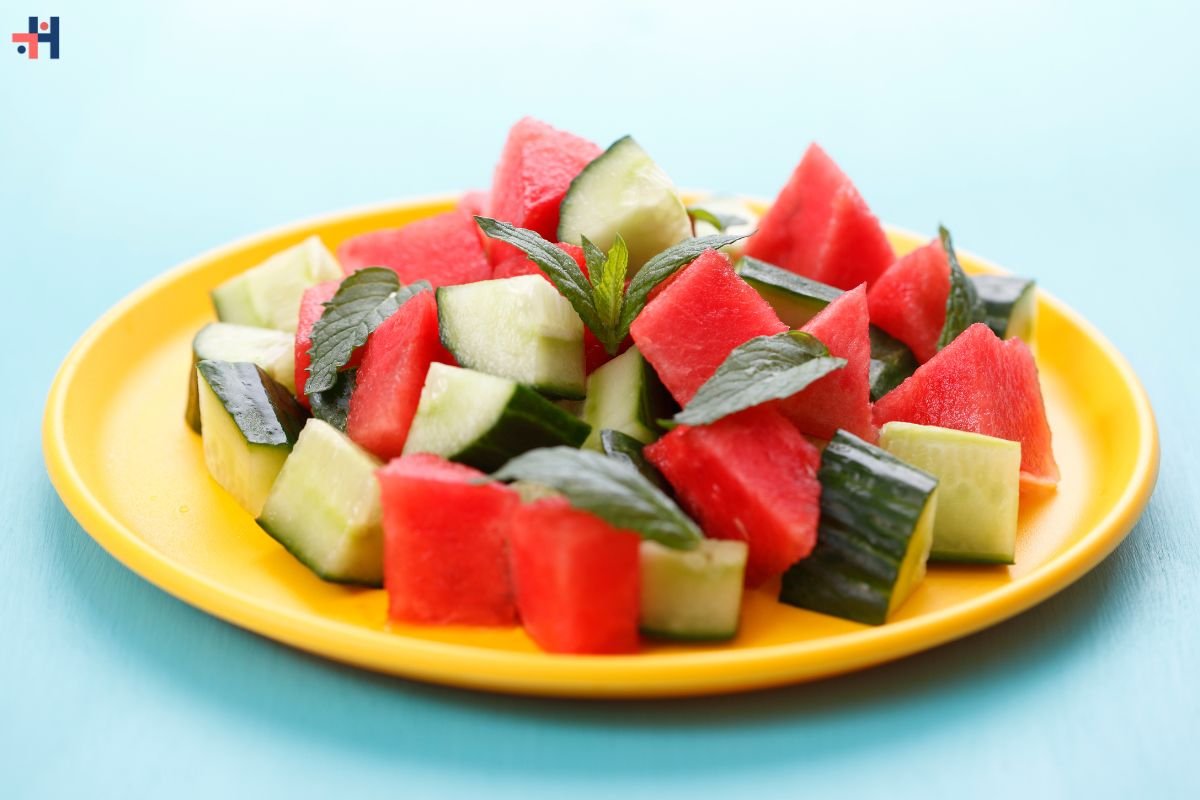

Preventing dehydration involves adopting healthy hydration habits:
- Drink Ample Fluids: Aim for at least 8 glasses (64 ounces) of water daily. Increase intake during hot weather or physical activity.
- Monitor Urine Color: Pale yellow urine indicates adequate hydration, while dark yellow urine suggests dehydration.
- Eat Water-Rich Foods: Incorporate fruits and vegetables like watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges into your diet to supplement fluid intake.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both can have a diuretic effect, increasing fluid loss.
- Stay Cool: Minimize exposure to extreme heat and take breaks in shaded or cool areas during hot weather.
Additional Symptoms and Signs of Dehydration in Adults
- Decreased Sweating: In severe dehydration, the body may stop sweating as it attempts to conserve remaining fluids.
- Low Blood Pressure: Dehydration can lead to a drop in blood pressure, causing symptoms such as light-headedness or fainting.
- Rapid Breathing: In cases of severe dehydration, rapid breathing may occur as the body tries to compensate for decreased oxygen levels.
- Fever: Dehydration can accompany illnesses that cause fever, exacerbating fluid loss.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Sodium and potassium levels can become imbalanced due to dehydration, leading to further complications.
When to Seek Medical Help
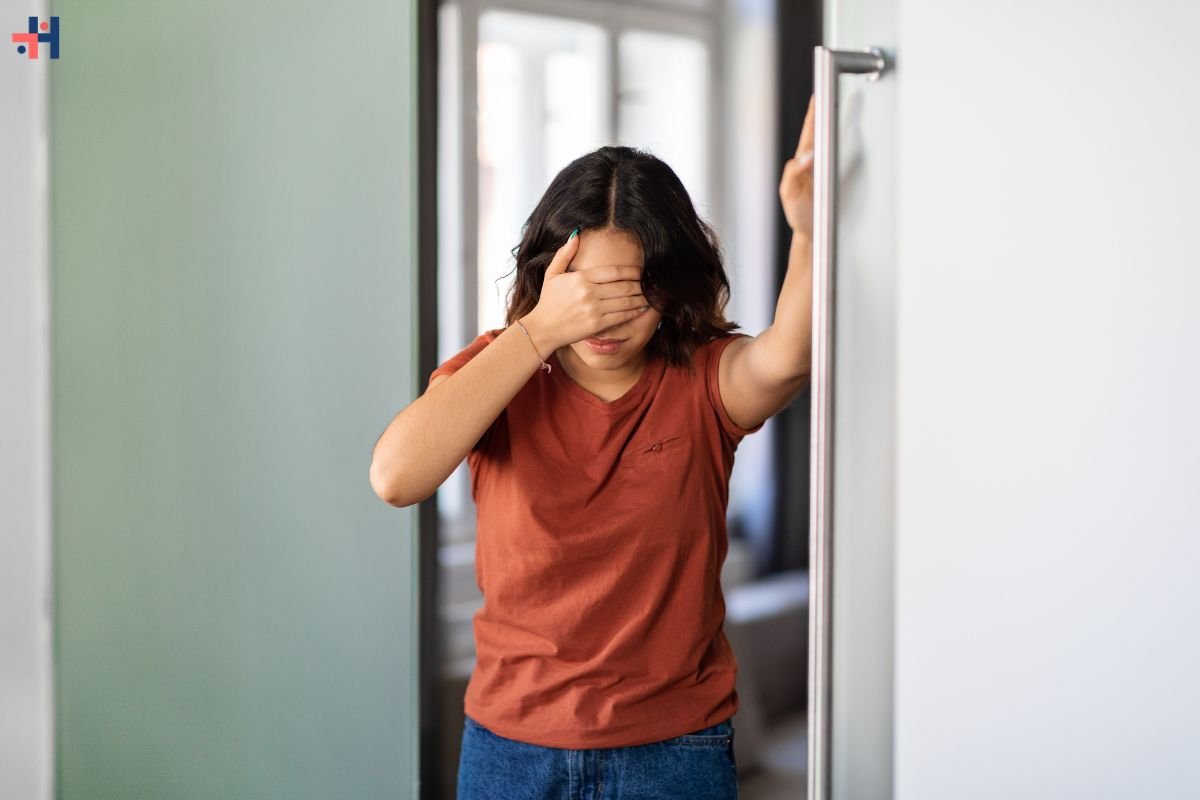

Prompt medical attention is crucial if you experience severe dehydration symptoms:
- Persistent Vomiting or Diarrhea: These can lead to rapid fluid loss.
- Inability to Keep Fluids Down: Difficulty keeping fluids down due to nausea or vomiting.
- Severe Weakness or Dizziness: Difficulty standing or walking due to weakness or dizziness.
- Confusion or Loss of Consciousness: Severe dehydration can impair cognitive function, leading to confusion or fainting.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of dehydration in adults and taking proactive steps to maintain adequate hydration is essential for overall health and well-being. By understanding the warning signals and adopting preventive measures, adults can effectively manage their hydration levels and reduce the risk of dehydration-related complications. Stay hydrated, stay healthy!
In conclusion, awareness of dehydration signs empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal hydration levels. By recognizing these signs early and adopting preventive measures, you can effectively manage your health and well-being.