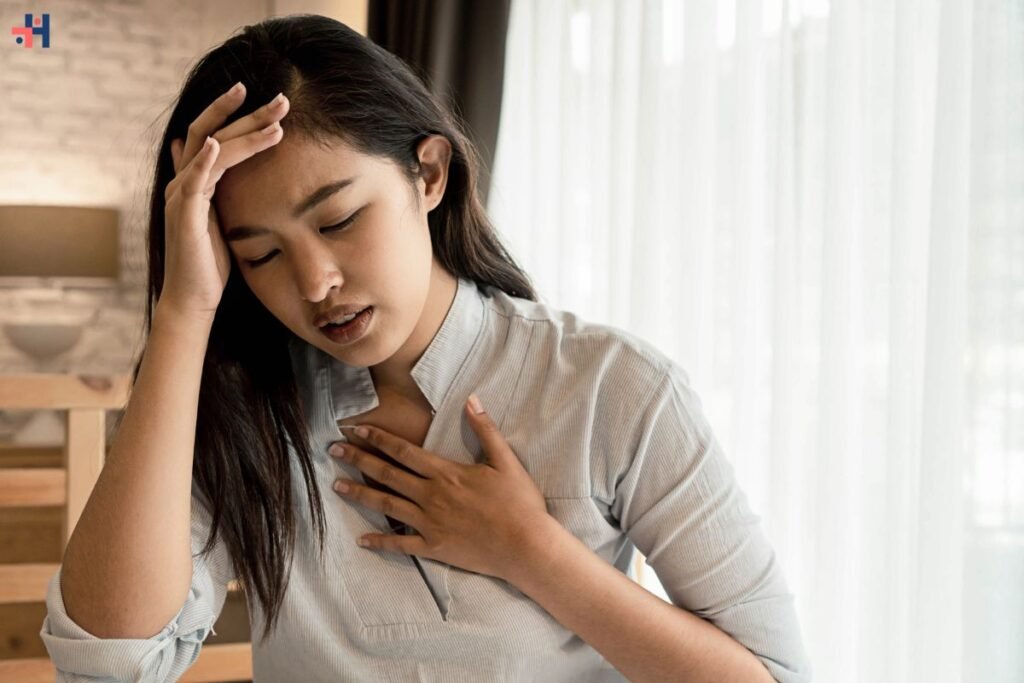
In the rhythm of our daily lives, few sensations disrupt the flow as profoundly as the abrupt gasp for air—shortness of breath. Whether it’s a fleeting episode or a persistent companion, this symptom demands attention, often serving as a silent alarm of underlying health concerns. Shortness of breath, medically termed dyspnea, transcends mere inconvenience; it’s a signal of potential distress within the intricate machinery of our bodies.
Understanding Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath encompasses a spectrum of sensations, from mild discomfort to crippling suffocation. It’s an umbrella term for the body’s response to various physiological or psychological triggers. The sensation can manifest as rapid, shallow breathing or a feeling of inability to draw in sufficient air, leading to anxiety and panic.
At its core, shortness of breath reflects an imbalance between oxygen supply and demand. This can arise from conditions affecting the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, or even psychological factors such as anxiety. Understanding the root cause is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Exploring Respiratory Causes

The respiratory system, tasked with the vital exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, is a common origin of shortness of breath. Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and pulmonary embolism can all restrict airflow or impair gas exchange, leading to dyspnea.
Asthma, characterized by airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction, often presents with episodes of wheezing and breathlessness. Similarly, COPD, primarily comprising chronic bronchitis and emphysema, progressively diminishes lung function, resulting in persistent dyspnea. Pneumonia, an infection of the lungs, and pulmonary embolism, a blockage in the pulmonary arteries, can both disrupt normal respiratory function, causing significant shortness of breath.
Unveiling Cardiovascular Contributions
Beyond the lungs, the cardiovascular system plays a pivotal role in oxygen delivery to tissues. Conditions such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmias can all precipitate dyspnea by impairing cardiac output or inducing fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Heart failure, a chronic condition characterized by the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently, often manifests with dyspnea, especially during exertion or when lying flat. Coronary artery disease, marked by the narrowing of blood vessels supplying the heart, can lead to angina (chest pain) and dyspnea, particularly during physical activity. Arrhythmias, irregular heart rhythms, can disrupt the heart’s pumping function, causing palpitations and breathlessness.
The Psychological Dimension

In addition to physiological factors, psychological influences can also trigger or exacerbate dyspnea. Anxiety disorders, panic attacks, and stress can heighten one’s perception of breathlessness, leading to a cycle of hyperventilation and further distress.
During moments of intense anxiety or panic, individuals may experience a sensation of suffocation, despite normal respiratory function. This phenomenon, known as psychogenic dyspnea, underscores the intricate connection between mind and body in shaping our experience of breathlessness.
Diagnostic Evaluation
Given the diverse array of potential causes, diagnosing the underlying reason for dyspnea requires a comprehensive approach. A thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests are often necessary to pinpoint the culprit.
Lung function tests, such as spirometry, can assess respiratory function and detect conditions like asthma or COPD. Imaging studies, including chest X-rays and CT scans, offer detailed insights into lung structure and pathology, aiding in the diagnosis of pneumonia or pulmonary embolism.
Cardiac evaluations, such as electrocardiography (ECG) and echocardiography, help assess heart function and identify conditions like heart failure or coronary artery disease. Blood tests may also be performed to evaluate oxygen levels, assess for infection or inflammation, and screen for risk factors such as elevated cholesterol or clotting disorders.
Also Read: Breathing Easy in the Face of Haboobs and Wildfires: 4 Essential Tips for Respiratory Health
Management and Treatment
Once the underlying cause is identified, management strategies can be tailored to address the specific condition contributing to dyspnea. This may involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
For respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD, bronchodilators and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce airway inflammation. Smoking cessation and avoidance of environmental triggers are also paramount in managing these conditions.

In heart failure, medications such as diuretics and ACE inhibitors help reduce fluid retention and improve cardiac function. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and regular exercise, can further support heart health and alleviate symptoms of dyspnea.
Psychological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and relaxation techniques, are beneficial for individuals experiencing psychogenic dyspnea or anxiety-related breathlessness. These approaches aim to address underlying triggers and equip individuals with coping strategies to manage distressing symptoms.
Conclusion
Shortness of breath, though often dismissed as a fleeting inconvenience, serves as a potent indicator of underlying health concerns. Whether stemming from respiratory, cardiovascular, or psychological origins, dyspnea demands attention and prompt evaluation.
By understanding the diverse array of factors contributing to breathlessness and adopting a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management, individuals can reclaim control over their respiratory health. Through targeted interventions and proactive measures, the silent alarm of shortness of breath can be met with informed action, ensuring optimal well-being and vitality.
FAQs:
1. What are common causes of shortness of breath?
Ans: Causes include respiratory issues like asthma and COPD, cardiovascular conditions, and psychological factors like anxiety.
2. When should I seek medical help for shortness of breath?
Ans: Seek help for sudden, severe breathlessness, especially with chest pain or fainting. Also, if it persists despite rest or worsens with activity.
3. How is shortness of breath diagnosed?
Ans: Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exams, lung function tests, imaging, cardiac evaluations, and blood tests.
4. What lifestyle changes can help ease shortness of breath?
Ans: Quit smoking, avoid triggers, maintain a healthy weight, and exercise regularly to support respiratory and heart health.
5. Are there self-care techniques for managing shortness of breath?
Ans: Try relaxation methods like pursed-lip breathing and stay hydrated. Use prescribed medications as directed. If symptoms persist, seek medical attention.