Source-rwandadispatch.com
Initiation of Vaccine Trials
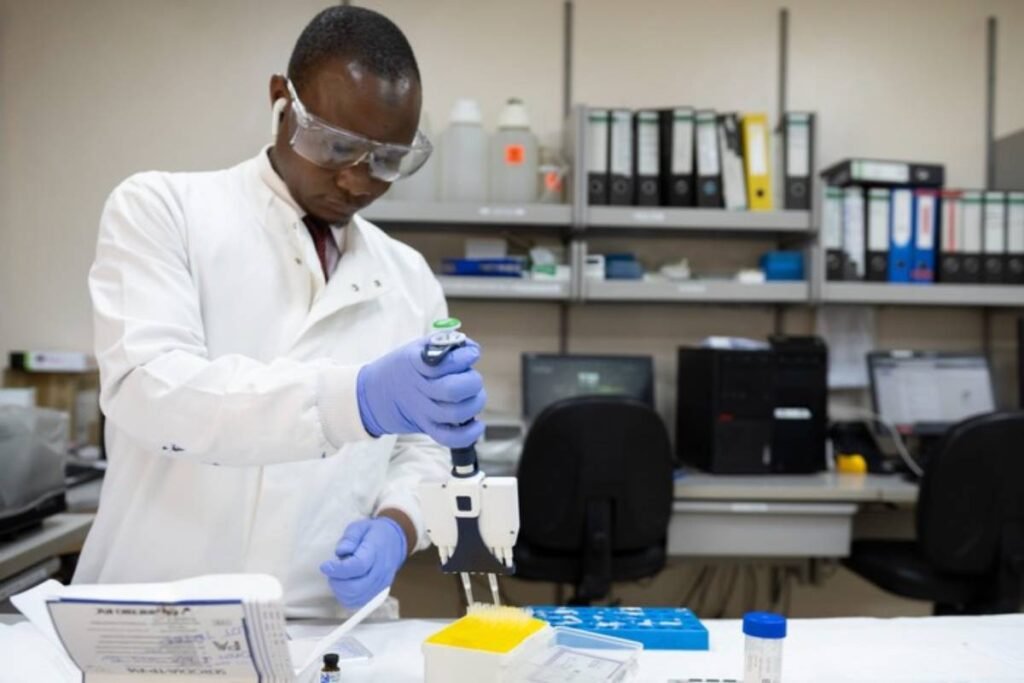
Rwanda has announced the commencement of vaccine trials for the deadly Marburg virus, which has already claimed the lives of at least 12 individuals in the country, with a significant number being healthcare workers. This move comes as the nation faces a growing public health crisis.
The East African nation has received 700 doses of the vaccine from the Sabin Vaccine Institute, a US-based non-profit organization dedicated to advancing vaccine research and development. The initial focus of the vaccination campaign will be on high-risk groups, including healthcare providers and individuals who have had contact with confirmed Marburg patients, according to Health Minister Sabin Nsanzimana.
Understanding Marburg Virus
The Marburg virus is highly infectious and shares similarities with the Ebola virus. Symptoms of the disease include fever, muscle pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and, in severe cases, death resulting from extreme blood loss. The health ministry reports that Rwanda has recorded at least 46 cases of Marburg, marking the first time the virus has been detected in the country. As of now, the source of the outbreak remains unknown.
Nsanzimana reassured the public regarding the vaccine’s safety, noting that trials have already been conducted in neighboring countries like Kenya and Uganda. While the vaccine has primarily been tested in adults aged 18 and older, there are currently no plans to include children in the trials.
Plans for Additional Doses and Precautions
The Rwandan government is also planning to order additional vaccine doses as part of its strategy to combat the outbreak. The World Health Organization (WHO) states that the Marburg virus has a fatality rate averaging around 50%, with past outbreaks showing mortality rates ranging from 24% to 88%.
In an effort to curb the spread of the virus, Rwandan authorities have implemented restrictions on the size of funerals for victims. These measures aim to prevent large gatherings that could facilitate further transmission of the virus.
Enhanced Health Measures and Travel Restrictions
To bolster its response, Rwanda is preparing to introduce travel restrictions. This will include temperature checks, passenger questionnaires, and hand-sanitizing stations at points of departure. These proactive measures are intended to monitor and reduce the risk of further outbreaks.
The Marburg virus is transmitted to humans from fruit bats and can spread through direct contact with the bodily fluids of infected individuals. Given its high transmission potential, swift action is critical to contain the outbreak.
Regional Context of Marburg Outbreaks
The situation in Rwanda follows a troubling trend in the region. Neighboring Tanzania reported an outbreak of the Marburg virus in 2023, while Uganda faced its own crisis in 2017, which resulted in the deaths of three individuals. These incidents underscore the need for vigilance and preparedness in dealing with infectious diseases.
As Rwanda embarks on this critical vaccine trial, the focus remains on protecting the health and safety of its citizens while addressing the urgent challenge posed by the Marburg virus. The government’s commitment to swift action and public health measures will be pivotal in navigating this health crisis and preventing further loss of life.