Neuropathic pain, often referred to as nerve pain or neuropathy, is a complex and challenging condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Unlike typical pain, which arises from tissue damage or inflammation, pain originates from dysfunction or damage to the nervous system. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of neuropathic pain, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Neuropathic Pain?
Neuropathic pain is characterized by shooting, burning, or stabbing sensations that can be chronic and debilitating. It occurs when nerves in the peripheral or central nervous system become damaged or malfunctioning, leading to abnormal signaling to the brain. This results in persistent pain that may be difficult to manage and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
Causes:
It can arise from various underlying conditions or injuries that affect the nervous system. Some common causes include:
- Diabetes: Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most prevalent causes of neuropathic disorder. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling, especially in the feet and hands.
- Traumatic Injury: Physical trauma, such as car accidents, falls, or sports injuries, can cause nerve damage and result in pain. Conditions like spinal cord injury or nerve compression can lead to chronic pain symptoms.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections, such as shingles (herpes zoster), HIV/AIDS, or Lyme disease, can damage nerves and trigger neuropathic pain.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune disorders like multiple sclerosis (MS) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can cause inflammation and damage to nerves, leading to neuropathic symptoms.
- Medications: Some chemotherapy drugs or medications used to treat HIV/AIDS can cause peripheral neuropathy as a side effect, leading to neuropathic pain.
- Hereditary Factors: In some cases, genetic factors may predispose individuals to neuropathic conditions, such as hereditary sensory neuropathy or Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
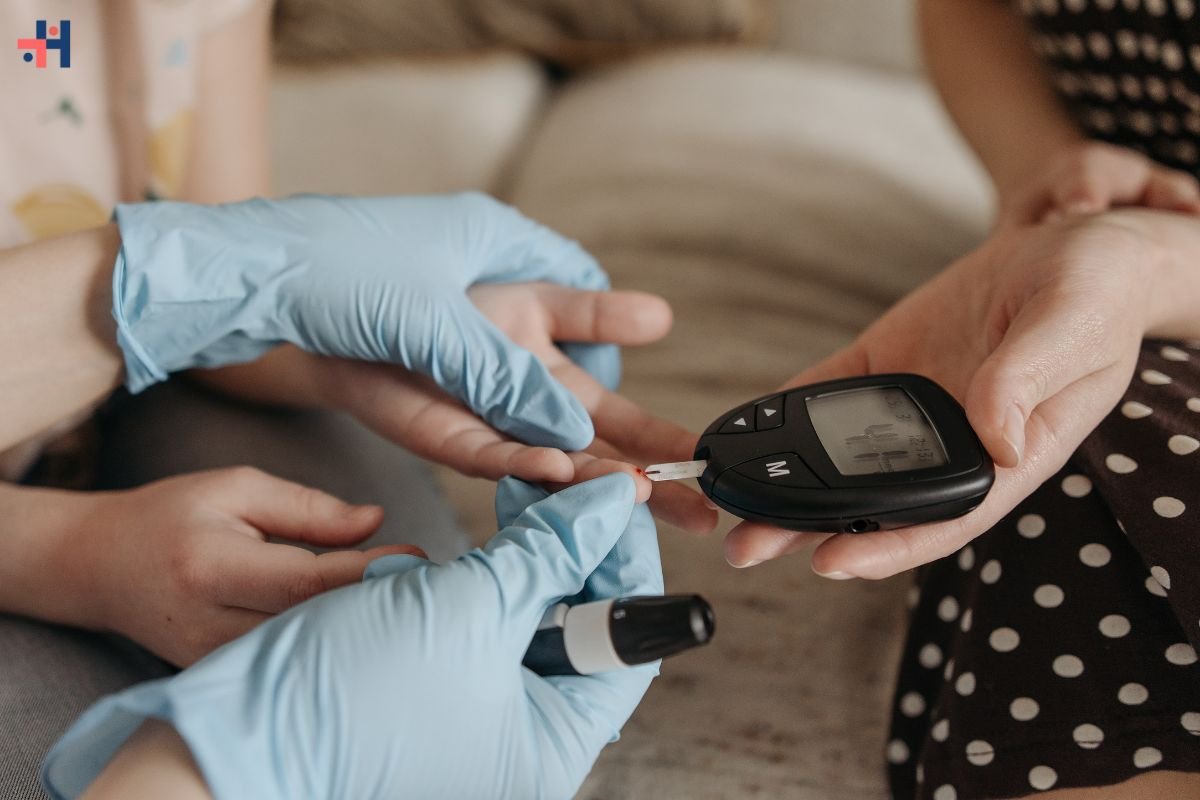
Symptoms:
The symptoms of neuropathic can vary depending on the underlying cause and affected nerves. However, common symptoms may include:
- Sharp, shooting, or burning pain
- Tingling or numbness
- Hypersensitivity to touch
- Electric shock-like sensations
- Muscle weakness or loss of coordination
- Difficulty sleeping due to pain
- Changes in temperature sensation
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing neuropathic requires a comprehensive medical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers may perform the following assessments:
- Medical History: Your doctor will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and any underlying conditions or injuries that may contribute to neuropathic pain.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination may help identify signs of nerve damage or dysfunction, such as decreased reflexes, muscle weakness, or sensory changes.
- Neurological Tests: Neurological tests, including nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG), can assess nerve function and identify areas of damage or dysfunction.
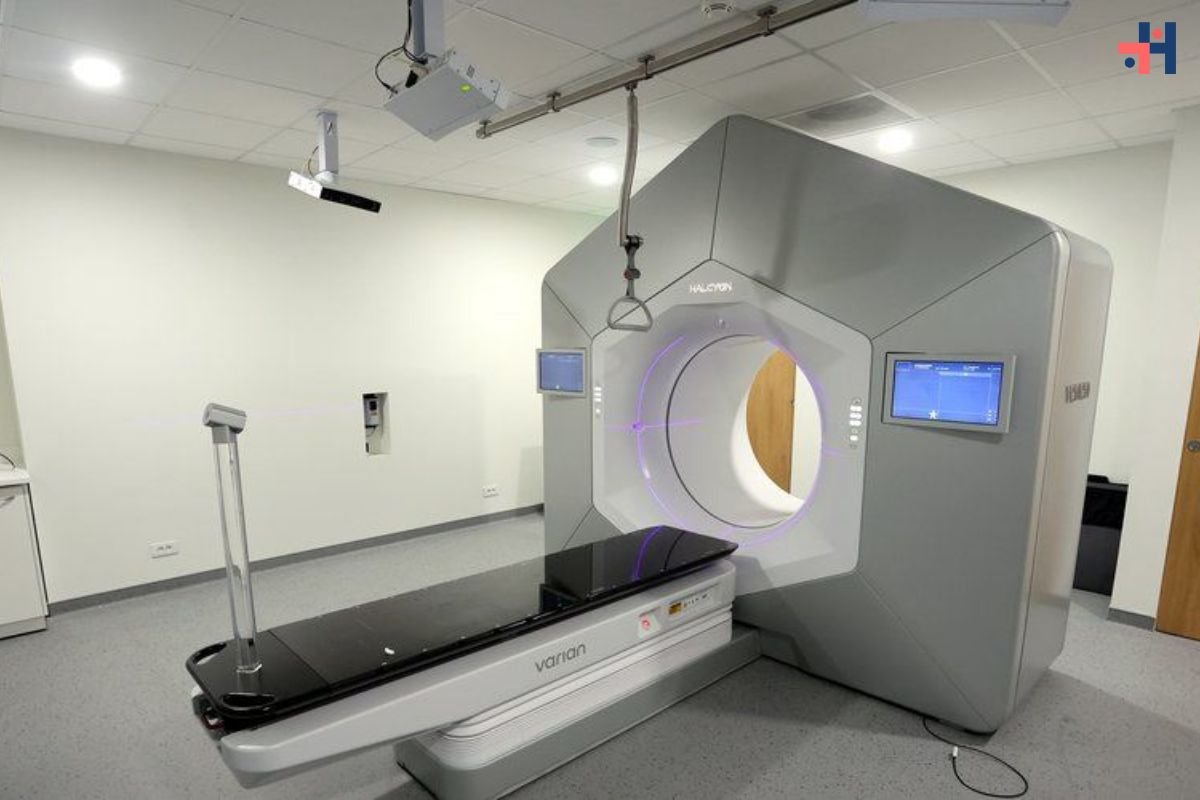
- Imaging Studies: Imaging tests like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be ordered to evaluate the structure of the nervous system and identify any underlying abnormalities or injuries.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to rule out underlying medical conditions or infections that could be contributing to neuropathic pain.
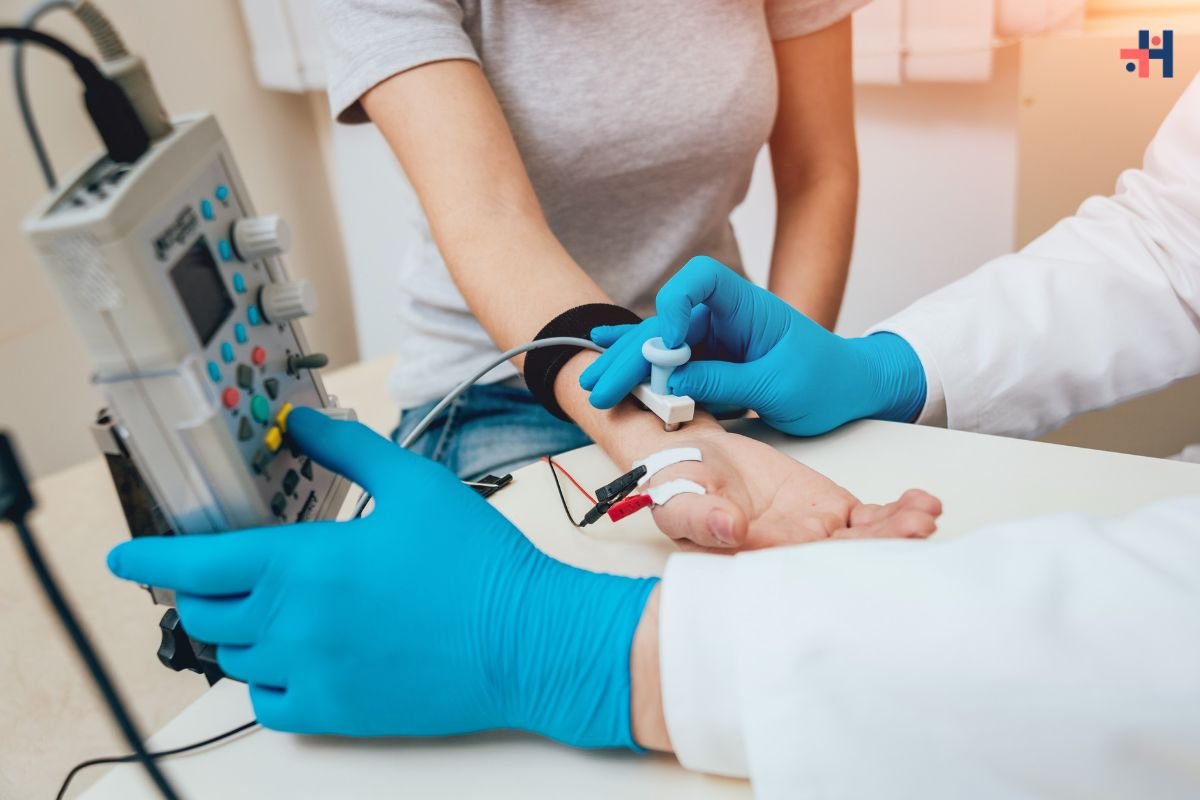
Also Read: Understanding Diabetic Foot Pain Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide
Treatment Options:
Managing such pain can be challenging, but various treatment options are available to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment approaches may include:
1. Medications:
- Antidepressants: Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), such as amitriptyline or nortriptyline, may help reduce neuropathic stress by altering neurotransmitter levels in the brain.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications like gabapentin or pregabalin can help stabilize nerve signals and reduce pain sensations.
- Topical Agents: Topical medications like lidocaine patches or capsaicin cream may provide localized pain relief.
- Opioids: In some cases, opioid medications may be prescribed for severe neuropathic pain that does not respond to other treatments. However, their use is often limited due to the risk of addiction and side effects.
2. Physical Therapy:
- Physical therapy techniques, such as gentle exercises, stretching, or massage therapy, can help improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion while reducing pain and discomfort.
3. Nerve Blocks:
- Nerve block injections, such as epidural steroid injections or local anesthetic injections, can temporarily block pain signals and provide relief for certain types of neuropathic pain.
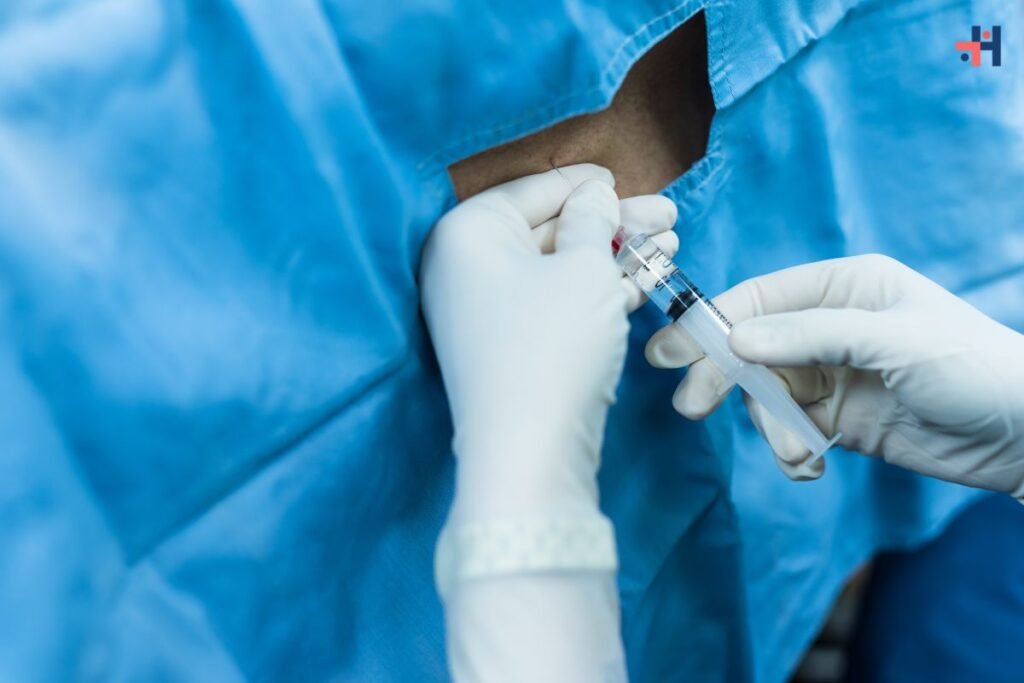
4. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS):
- TENS therapy involves the use of a small device that delivers low-voltage electrical currents to the skin, which may help disrupt pain signals and provide relief.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco, can help reduce inflammation, improve nerve function, and alleviate neuropathic symptoms.
6. Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture, acupressure, and chiropractic care are alternative therapies that some individuals find helpful in managing neuropathic pain. While the scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is mixed, they may provide relief for some individuals.
Conclusion:
Neuropathic pain is a complex and challenging condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. By understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, individuals can work with healthcare providers to develop personalized management plans tailored to their needs. With the right approach, it is possible to effectively manage pain and improve overall well-being. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of neuropathic pain, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.