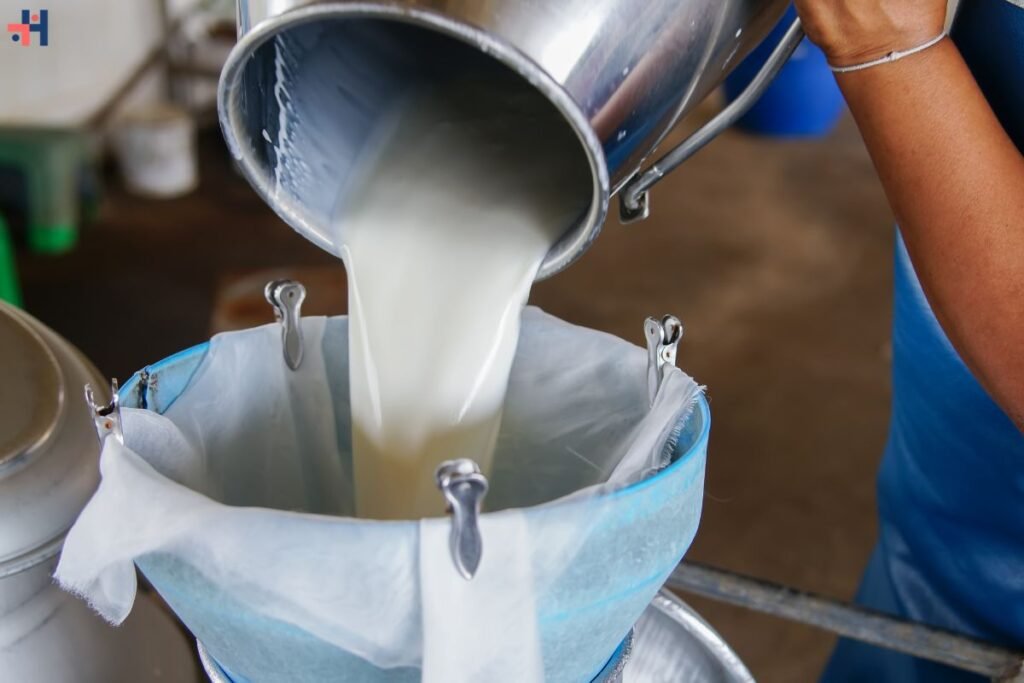
Raw milk, milk that has not been pasteurized or homogenized, has garnered significant attention in recent years. Advocates tout its health benefits, while critics raise concerns about safety. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the health benefits of raw milk, separating myths from facts and providing a balanced perspective on its consumption.
Nutritional Profile of Raw Milk
Raw milk is praised for its rich nutritional content. It contains a variety of vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and beneficial bacteria that contribute to overall health. Some of the key nutrients found in raw milk include:
Vitamins and Minerals: Raw milk is an excellent source of essential vitamins such as A, D, E, and K, as well as minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
Enzymes: It contains enzymes like lipase and phosphatase, which aid in the digestion of fats and absorption of calcium.
Probiotics: The beneficial bacteria present in raw milk can promote a healthy gut microbiome and enhance digestive health.
Proteins and Fats: Raw milk provides high-quality proteins and healthy fats, including omega-3 fatty acids.
Health Benefits of Raw Milk
Advocates of raw milk claim that it offers several health benefits that are diminished or lost during pasteurization. Here are some of the purported benefits:
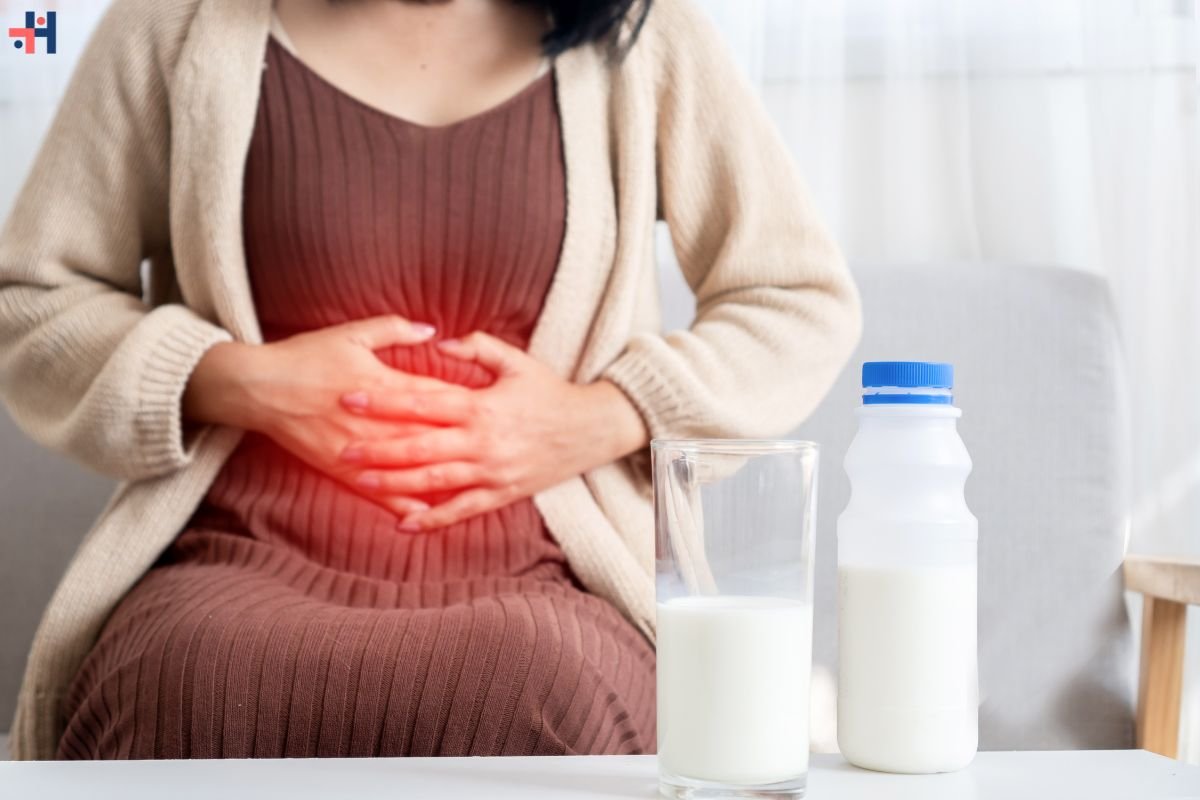

- Enhanced Digestive Health: Raw milk contains a diverse array of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that support gut health. These probiotics can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, improve digestion, and alleviate symptoms of lactose intolerance for some individuals.
- Improved Immune Function: The presence of immunoglobulins and lactoferrin in raw milk is believed to bolster the immune system. These components have antimicrobial properties that can help fight infections and support overall immune function.
- Better Nutrient Absorption: Proponents argue that the enzymes in raw milk facilitate better digestion and absorption of nutrients. For instance, lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose, is naturally present in raw milk and may help those with lactose sensitivity.
- Bone Health: The high calcium content in raw milk, combined with the presence of vitamin K2, is thought to enhance bone health. Vitamin K2 plays a crucial role in calcium metabolism and helps direct calcium to the bones where it is needed.
- Skin Health: Some anecdotal evidence suggests that consuming raw milk can improve skin conditions such as eczema and acne. This is attributed to the presence of beneficial fats, vitamins, and probiotics that promote skin health from the inside out.
Safety Concerns and Risks
Despite the potential health benefits, raw milk also carries significant risks. One of the primary concerns is the potential for contamination with harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. These pathogens can cause severe illness, particularly in vulnerable populations like children, pregnant women, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems.
Regulatory Perspectives
Different countries and states have varying regulations regarding the sale and consumption and health benefits of raw milk. In the United States, for example, the sale of raw milk is heavily regulated, with some states allowing it only for pet consumption, while others permit sales directly from farms. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and CDC strongly advise against the consumption of raw milk due to the potential health risks.
Consumer Considerations

For those considering raw milk, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the risks. Here are some important considerations:
- Source Quality: If you decide to consume raw milk, ensure it is sourced from a reputable, certified organic farm with stringent hygiene practices and regular testing for pathogens.
- Personal Health: Individuals with compromised immune systems, young children, pregnant women, and the elderly should avoid raw milk due to the increased risk of foodborne illness.
- Informed Decision: Make an informed decision by consulting with healthcare professionals and conducting thorough research on both the benefits and risks associated with raw milk.
Alternatives to Raw Milk
For those seeking the health benefits associated with raw milk but without the risks, there are alternatives available. Pasteurized milk products, such as kefir, yogurt, and cheese, contain beneficial probiotics and nutrients. Additionally, some dairies offer low-heat pasteurized milk, which retains more of the beneficial enzymes and bacteria compared to traditional pasteurization methods.
Conclusion: Balancing Health Benefits of Raw Milk and Risks
Raw milk remains a contentious topic, with passionate advocates on both sides of the debate. While it offers several potential health benefits, it also carries significant risks due to the potential for bacterial contamination. Consumers must carefully weigh these factors and make informed choices based on their individual health needs and preferences. For those seeking the benefits of raw milk with fewer risks, exploring pasteurized dairy products with added probiotics may be a safer alternative. In the evolving landscape of nutrition and health, it is crucial to stay informed and critically evaluate new information. Whether you choose to incorporate health benefits of raw milk into your diet or opt for pasteurized alternatives, understanding the science behind the claims can help you make the best decisions for your health and well-being.









